Brief content
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) is a hard fork of the Go Ethereum (Geth) protocol, which has a lot in common with the Ethereum blockchain. However, the developers of the BSC made significant changes in some key areas. The biggest change is the BSC consensus mechanism, which allows for cheaper and faster transactions.
Introduction
At first glance, Binance Smart Chain (BSC) and Ethereum look very similar. DApps and tokens built on BSC are compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). You may have noticed that your public wallet addresses are the same on both blockchains. There are even cross-chain projects that work on both networks. However, there are notable differences between the two circuits. If you're wondering which one to use, it's best to know and understand the differences.
Blockchain traffic and DApp ecosystem
As of June 2021, Ethereum has over 2,800 DApps on the blockchain compared to around 810 DApps on the BSC. This is a significant difference, but considering the young age of BSC, the network shows a strong and growing ecosystem.
Active addresses are also an important indicator in the network. Despite being a newer blockchain, BSC registered 2,105,367 addresses on June 7, 2021, more than double Ethereum's all-time high of 799,580 addresses on May 9, 2021.
So what exactly is the reason for the sudden massive growth of BSC? This is largely due to faster confirmation times and low fees. BSC's growth can also be attributed to the growing hype surrounding NFTs and compatibility with popular cryptocurrency wallets such as Trust Wallet and MetaMask.
If we look at daily transactions, the difference between the two is even greater. In BSC, users can move their funds faster and more economically and interact with smart contracts. Below you can see BSC's peak of around 12 million daily transactions and the current status of over four million.
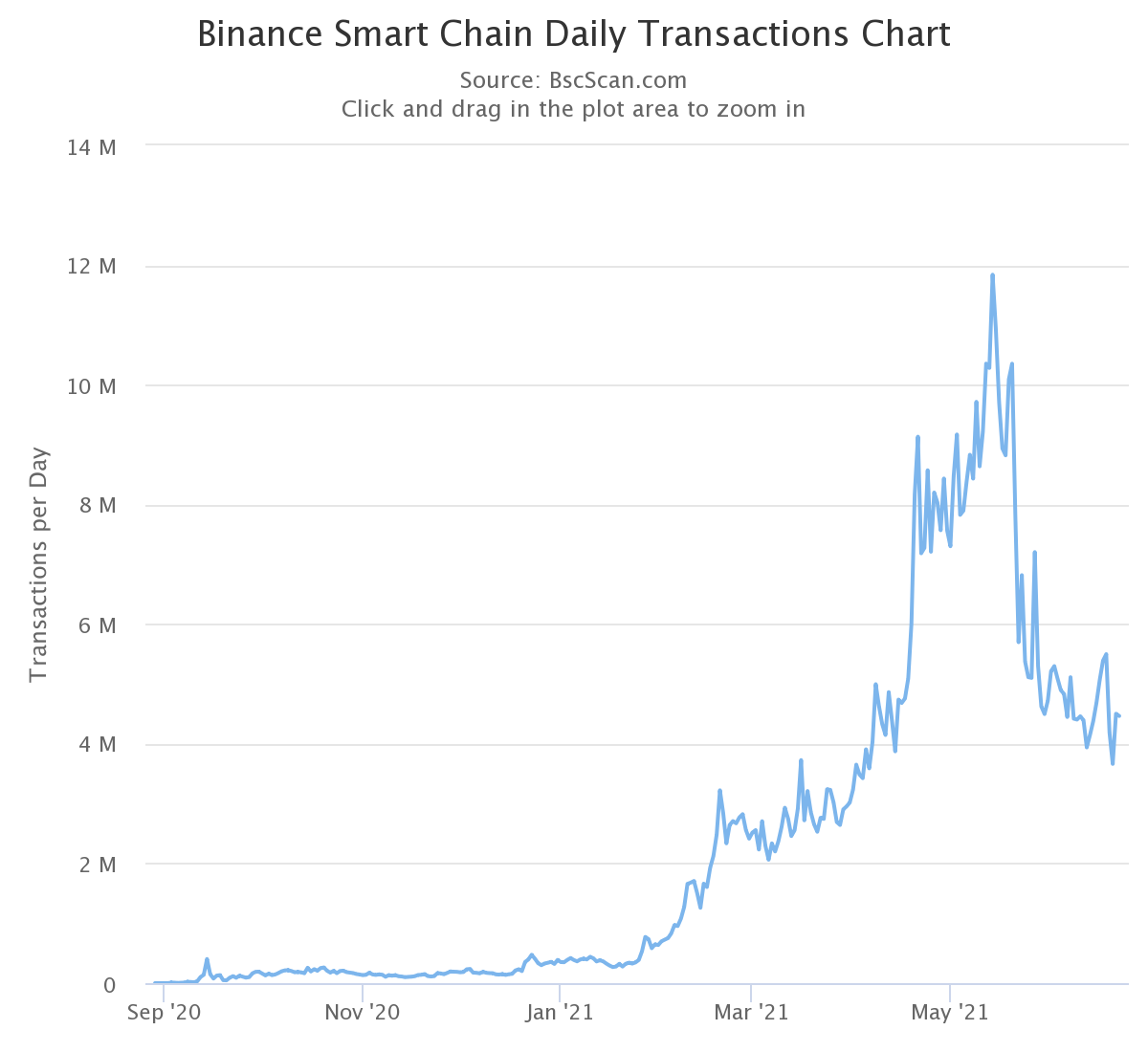
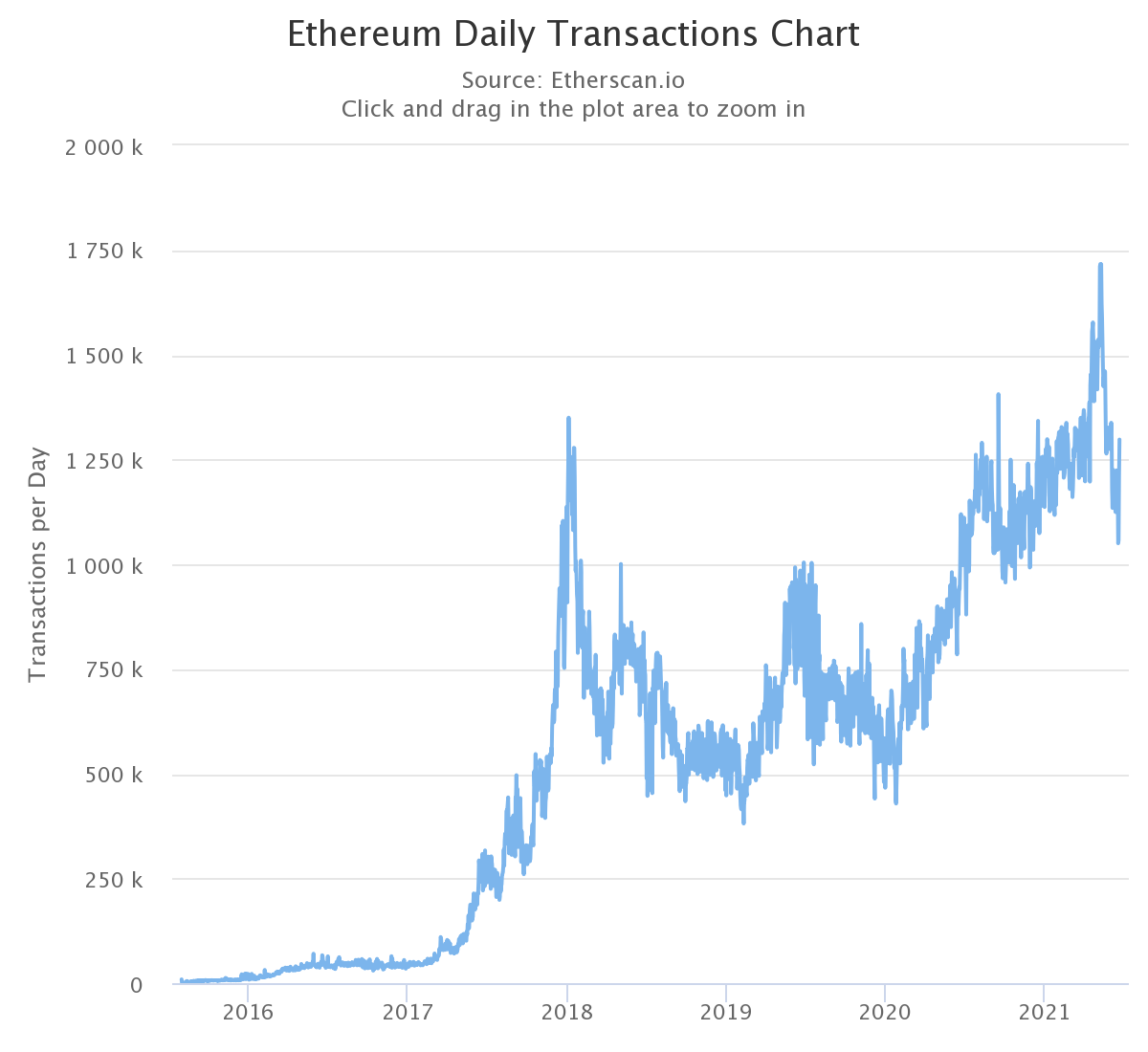
On the other hand, the number of transactions in Ethereum has never exceeded 1.75 million transactions per day. For users who need to transfer their funds regularly, BSC will be a more popular choice. Daily transactions must also be considered in the context of active addresses. At the time of writing, BSC has more users who also average more transactions.
The most used DeFi DApps on Ethereum and BSC
When it comes to decentralized finance, there are a large number of DApp interweaves between BSC and Ethereum due to blockchain compatibility. Developers can easily port applications from Ethereum to BSC, and new BSC projects often reuse the open source code from Ethereum under a different name. Let's take a look at the top five DApps on Ethereum according to DAppRadar users.
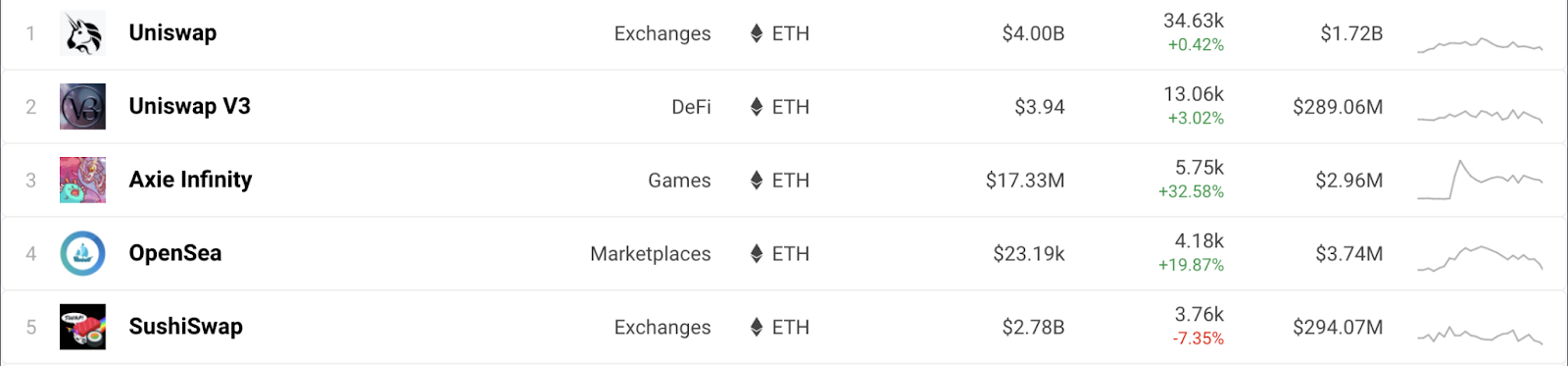
Here you can see a mixture of two DeFi automatic market makers (Uniswap and SushiSwap), a crypto game (Axie Infinity), and a peer-to-peer marketplace (OpenSea). If you look at the top five BSCs, you will see a lot in common.

PancakeSwap was created as a hard fork of Uniswap. Autofarm and Pancake Bunny represent a profitable farm, a category we don't see in the top five on Ethereum. Biswap and Apeswap are automated market makers. Because BSC fees are so low and transactions are so much faster, profitable farming is generally more efficient on Binance Smart Chain. These factors make them a popular choice for BSC users.
When it comes to crypto games, Ethereum is indeed home to the most popular games. Although there are projects on BSC very similar to CryptoKitties and Axie Infinity, they have not been able to attract as large an audience as the classic games on Ethereum.
Transfers between networks
If you have made any BEP-20 or ERC-20 deposit to your wallet, you may have noticed that your Ethereum and BSC wallet addresses are identical. So, for example, if you choose the wrong network when withdrawing tokens from an exchange, you can easily get them back from another blockchain.
If you accidentally withdraw an ERC-20 token on BSC, you can still find them at the corresponding BSC address. You can also go through the same process if you accidentally send tokens from BSC to Ethereum. In both cases, your funds are fortunately not lost forever. For a more detailed guide, check out How to Recover Cryptocurrency Transferred to the Wrong Network on Binance.
Transaction fees
BSC and Ethereum use the gas model for transaction fees that measure their complexity. BSC users can set the price of gas according to the needs of the network, and miners will prioritize transactions with higher gas prices. However, the London hard fork for Ethereum introduces some new modifications that will likely eliminate the need for high fees.
The Ethereum update creates a new pricing mechanism with a basic block fee. The base fee varies depending on the demand for transactions, eliminating the need for users to determine the gas price themselves.
Historically, Ethereum gas fees have been much higher than BSC. The highest average indicator was in May 2021 - $68.72. This trend has started to change, but Ethereum is currently still more expensive.
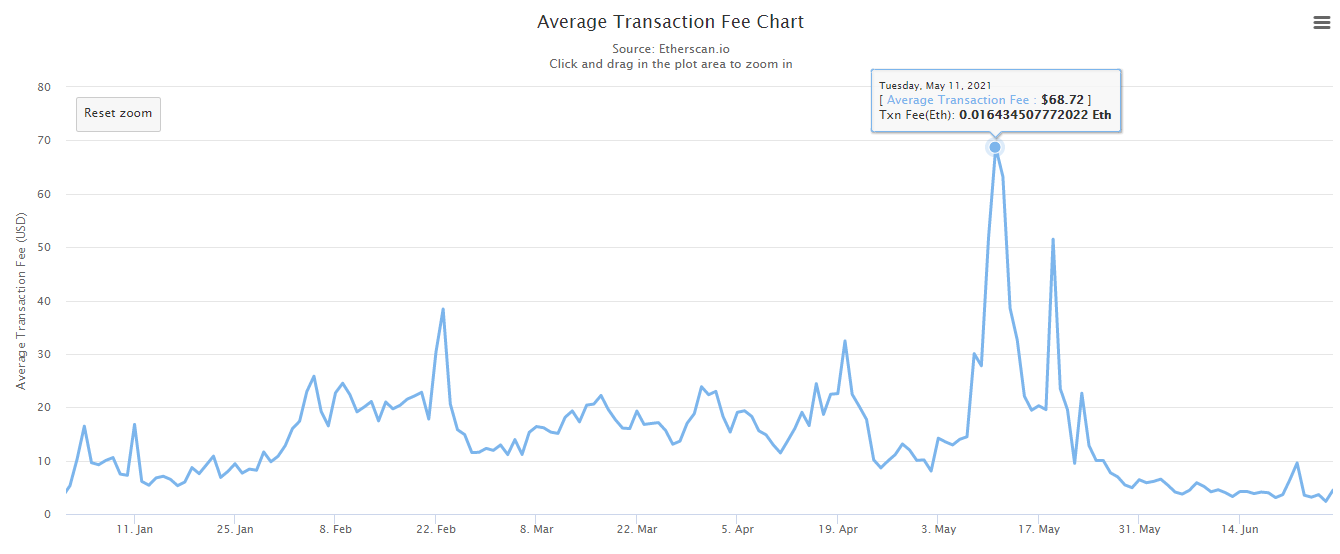
Let's take a look at the average Ethereum costs from Etherscan to get a better idea. The top three numbers show the current Ethereum gas prices. For both BSC and Ethereum, one gwei is equal to 0.000000001 BNB or ETH respectively. If you pay a lower price, your transaction will take much longer.
The average price of simply transferring an ERC-20 token to another wallet at the time of writing is $2.46. This number increases to $7.58 when using Uniswap's liquidity pool, which includes multiple transactions.

Below we can see a BSC transaction with a fee of only $0.03, which is equivalent to an ERC-20 transfer in the gas tracker on Ethereum. BSC calculated this by multiplying the amount of gas used for the transaction (21,000) by the price of gas (5 gwei).
Transaction time
Measuring average transaction times on blockchains can be a bit tricky. Although a transaction is technically complete after miners verify the block it is in, other aspects can affect the waiting time:
If you don't set a high enough fee, miners may delay your transaction or even block it.
More complex blockchain interactions require multiple transactions. For example, adding liquidity to a liquidity pool.
Most services will consider a transaction valid only after a certain number of blocks have been confirmed. These additional confirmations reduce the risk of chargebacks by merchants and service providers if the block is rejected by the network.
If we look above at the gas statistics for Ethereum, we can see that the transaction time varies from 30 seconds to 16 minutes. These numbers take into account successful transactions, but do not require additional confirmations.
For example, if you deposit ETH (ERC-20) to your Binance account, you will need to wait for 12 network confirmations. If a block is mined approximately every 13 seconds, as you can see in the graph below, this will add an extra 156 seconds when depositing ETH to your spot wallet.

On BSC, the average block time is 3 seconds. When we compare this to Ethereum's 13 seconds, we see a speed increase of about 4.3 times.

Consensus mechanism
Although Ethereum's Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism is similar to Bitcoin's, it is very different from the Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA) used by BSC. However, this difference will not last long. With the Ethereum 2.0 update, the network will start using the Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism.
PoSA BSC combines aspects of Proof of Authority (PoA) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS). 21 validators take turns creating blocks and, in turn, receive a BNB transaction fee as a reward. To become a validator, you need to start a node and stake at least 10,000 BNB, after which you become a selected candidate.
Other users, known as delegators, stake BNB for the chosen candidate. 21 candidates, selected by the amount of staking, will take turns processing the blocks. This whole process is repeated every 24 hours. Delegators also receive a portion of the rewards that validators earn.
PoW Ethereum is a completely different system. Instead of the community electing validators, there is a race to solve a computational puzzle. Anyone can participate, but they will need to buy or rent specialized mining equipment. The more computing power you have, the more likely you are to be the first to solve the puzzle and confirm the block. Successful miners receive a transaction fee and reward in ETH.
Although PoW is an effective way to achieve consensus and ensure network security, developers have since explored the use of other mechanisms. Their goal is to find more efficient and environmentally safe alternatives without compromising safety.
For these reasons, the Ethereum network will eventually move to Proof of Stake. Validators stake ETH to be able to produce blocks. Other validators will "witness" the block and check its correctness. If someone creates a block that contains false transactions, they risk losing all their staking coins. Validators are then rewarded for successful blocks and any validations they make. By making direct deposits and staking large amounts of ETH, malicious validators risk losing their funds.
Final thoughts
It is clear that Binance Smart Chain and Ethereum have a lot in common. Especially because Ethereum users can easily migrate from Ethereum and start experimenting with BSC. But despite the similarities, BSC has made some interesting changes to try to improve performance and efficiency. The Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA) consensus mechanism allowed users to get even cheaper and faster blockchain transactions.





