Contents
Cryptocurrencies for dummies
How does a blockchain work?
How to invest in cryptocurrencies?
Frequently asked questions about cryptocurrencies
Chapter 1 - Cryptocurrency for Dummies
Contents
What is a cryptocurrency?
What makes cryptocurrencies unique?
Why the name “cryptocurrency”?
What is public key cryptography?
Who invented cryptocurrencies?
What is the difference between cryptocurrencies and tokens?
What is a crypto wallet?
What is a cryptocurrency?
A cryptocurrency (or “crypto”) is a form of digital currency that allows individuals to transmit value in a digital universe.
You may be wondering how this type of system differs from PayPal or the digital banking app you have on your phone. They certainly seem to meet the same use cases: paying friends, making purchases on your favorite website. They are, however, very different, if you observe them carefully.
What makes cryptocurrencies unique?
Cryptocurrencies are unique for many reasons. their primary function, however, is to serve as an electronic money system that does not belong to anyone.
A good cryptocurrency must be decentralized. There is no central bank or subset of users that can change the rules without reaching consensus. Network participants (nodes) run software that connects them to other participants so that they can share information with each other.
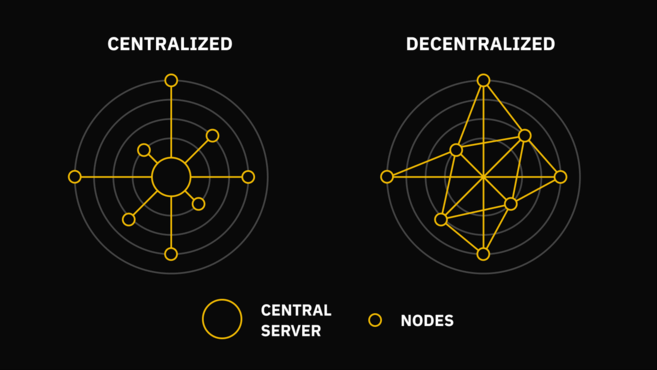
Centralized or decentralized networks.
On the left, this is what you would expect to see used by a bank, for example. Users must communicate through a central server. On the right, there is no hierarchy: the nodes are interconnected and relay information between them.
The decentralization of cryptocurrency networks makes them highly resistant to forced shutdowns or censorship. On the other hand, to make a centralized network inoperable, all you need to do is jam the main server. If a bank had wiped its database and there were no backups, it would be very difficult to determine user balances.
In cryptocurrencies, nodes maintain a copy of the database. Everyone acts as their own server. Individual nodes may be disconnected, but their peers will still be able to obtain information from other nodes.
Cryptocurrencies are therefore functional 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. They enable the transfer of value anywhere in the world, without the intervention of intermediaries. That's why we often call them permissionless: anyone with an Internet connection can transfer funds.
Why the name “cryptocurrency”?
The term “cryptocurrency” is a portmanteau made up of the terms cryptography and currency. This is simply because cryptocurrencies use many cryptographic techniques to secure transactions between users.
What is public key cryptography?
Public key cryptography relies on cryptocurrency networks. This is what users rely on to send and receive funds.
In a public key cryptography scheme, we have a public key and a private key. A private key is a very long number that is impossible to guess. It is often difficult to imagine in your head the size of this number.
For Bitcoin, guessing a private key is as likely as correctly guessing the outcome of 256 successive coin tosses. With today's computers, you wouldn't even be able to crack someone's key before the universe died.
Anyway, as the name suggests, you need to keep your private key secret. But from this key you can generate a public one. This can be shared with anyone. It is completely impossible to trace the private key from the public key.
You can also create digital signatures by signing data with your private key. It is an action analogous to signing a document by hand. The main difference is that anyone can tell if a signature is valid by comparing it to the public key. The user therefore never needs to reveal his private key, but can still prove that he owns it.
In cryptocurrencies, you can only spend your funds if you have the corresponding private key. When you make a transaction, you announce to the network that you want to move your funds. This is announced in a message (i.e. a transaction), which is signed and added to the cryptocurrency database (the blockchain). As mentioned, you need your private key to create the digital signature. Since anyone can view the database, they can check if the transaction is valid by checking its signature.
Who invented cryptocurrencies?
Many attempts to create digital money concepts have emerged over the years, but the first cryptocurrency to emerge was Bitcoin, in 2009. It was created by a person or group calling themselves Satoshi Nakamoto. To this day, his true identity remains unknown.
Bitcoin led to the subsequent creation of a very large number of cryptocurrencies, some aiming to compete with Bitcoin, others seeking to integrate features that were not available with Bitcoin. Today, many blockchains not only allow users to send and receive funds, but also run decentralized applications using smart contracts. Ethereum is perhaps the most popular example of such a blockchain.
What is the difference between cryptocurrencies and tokens?
At first glance, cryptocurrencies and tokens seem identical. Both are traded on exchanges and can be transferred between blockchain addresses.
Cryptocurrencies are exclusively intended to be used as currency, whether as a store of value, or as currency, or both. Each unit is functional and fungible, meaning that one unit of currency is worth as much as another.
Bitcoin and other early cryptocurrencies were designed as currencies, but later blockchains sought to do more. Ethereum, for example, doesn't just provide currency functionality. It allows developers to execute code (smart contracts) on a distributed network and create tokens for a variety of decentralized applications.
Tokens can be used like cryptocurrencies, but they are more flexible. You can create millions of identical ones or select a few with unique properties. They can have any purpose, from digital receipts representing ownership in a business to loyalty points.
On a protocol compatible with smart contracts, the base currency (used to pay for transactions or applications) is distinct from its tokens. On Ethereum, for example, the native currency is Ether (ETH), and it must be used for the creation and transfer of tokens within the Ethereum network. These tokens are implemented according to standards such as ERC-20 or ERC-721.
What is a crypto wallet?
Basically, a crypto wallet is something that contains your private keys. It could be a specially designed device (a hardware wallet), an app on your PC or smartphone, or even a piece of paper.
The wallet is an interface through which most users will be able to interact with a network of cryptocurrencies. Different types of wallets offer different functionality: Obviously, a paper wallet cannot sign transactions or display current prices in fiat currency.
For practical reasons, software wallets (e.g. Trust Wallet) are considered superior when it comes to everyday payments. For security purposes, hardware wallets are virtually unmatched in their ability to keep private keys away from prying eyes. Cryptocurrency users tend to keep their funds in both types of wallets.
Chapter 2 - How does blockchain work?
Contents
What is blockchain?
How are blocks added to a blockchain?
How does crypto mining work?
Can cryptocurrencies evolve (scale)?
Who Makes Decisions About Cryptocurrency Software?
What is blockchain?
A blockchain is a special type of database in which data can only be added (and not deleted or modified). Transactions are periodically added to a blockchain inside what we call blocks (made up of transaction information and other important metadata).
We call this structure a "chain" because each block's metadata includes an element of information that links it to the previous block. Specifically, it includes a hash of the previous block, much like a unique fingerprint.
The probability that two datasets will give you the same result from a hash function is infinitesimally small. Therefore, if someone tried to modify an old block, its hash would be different, which means the hash of the next block would also be different, and so on. It is therefore obvious that a block has been modified, because all the blocks following it will also be modified.

The hash of each block is included in the next block. This forms the block chain, or blockchain.
The blockchain is downloaded in its entirety by network participants. Remember how we mentioned that anyone can validate transactions and signatures with public key cryptography? When a node receives a block, it performs a number of checks. If any element is invalid, the block is rejected.
When a node receives a valid block, it makes its own copy of it and then propagates it to other nodes. They then do the same until the block has spread throughout the network. This process is also carried out for unconfirmed transactions, i.e. transactions that have been broadcast, but are not yet included in the blockchain.
See also: What is Blockchain Technology? The ultimate guide.
How are blocks added to a blockchain?
The integrity of a blockchain is undermined when false financial information can be recorded. There is also no administrator or manager in the distributed system that maintains the database, so how can we ensure that participants act honestly?
Satoshi proposed a proof-of-work system, which allowed anyone to suggest a block to add to the blockchain. To find a block, users must sacrifice computing power to guess the answer to a protocol-defined challenge.
Proof of work is the most proven system for achieving consensus among users, but it is not the only one. Alternatives such as proof of stake are increasingly being studied, although they have not yet been properly implemented in their actual form (although hybrid consensus mechanisms have existed for some time).
See also: What is a blockchain consensus algorithm?
How does crypto mining work?

The process described above is called mining. If the miner finds a solution, the block he built extends the chain. As a result, he will receive a reward denominated in the blockchain's native currency.
The cryptographic puzzle that miners must solve involves repeatedly hashing data to produce a number less than a given value. Hashing with a one-way function means that it is virtually impossible to guess the input data from the result. But given the input, it is trivial to check the result. Thus, any participant can verify that the miner has produced a “correct” block and rejects those that are invalid. In this case, the miner receives no reward and has wasted resources trying to forge an invalid block.
The result is an interesting game theory that makes any attempt at falsification very costly, while making honest behavior very profitable. No malicious entity has enough resources to attack a strong network for an indefinite period of time. Thus, it is assumed that participants will make honest use of their resources in order to be profitable.
See also: What is cryptocurrency mining?
Can cryptocurrencies evolve (scale)?
As you probably suspect by now, distributed networks are not very efficient. Unfortunately, cryptocurrencies can only be secure and censorship-resistant if all nodes are able to synchronize a copy of the blockchain. The lower the requirements for keeping up, the easier it will be for people to participate.
You can understand why a blockchain that only adds a small block every ten minutes is preferable, in this regard, to a blockchain that adds a huge block every five minutes. In the second case, the nodes would have to run very powerful computers to stay synchronized, the less powerful computers would disconnect. This would lead to greater centralization, as there would be fewer peers on the network.
But with small blocks, the number of transactions per second (TPS) is more limited. This means that in periods of high activity, transactions can take a long time to be added to the blockchain. This is inconvenient when you want to make a quick payment, but that's the price you pay for decentralization.
We call this problem the scalability dilemma. A system that scales well is one that can easily adapt to increased throughput with minimal inconvenience. Blockchains cannot scale ideally. As we've explained, simply increasing throughput with larger blocks undermines the very purpose of a distributed network.
To increase the number of TPS without harming network decentralization, off-chain scaling appears to be a viable approach. This encompasses a wide range of solutions, centralized and decentralized, that allow transactions to be carried out without recording them on the blockchain.
Check out some examples of off-chain scalability: Blockchain Scalability: Sidechains and Payment Gateways.
Who Makes Decisions About Cryptocurrency Software?
Cryptocurrency networks are opt-in, no one forces you to run software you don't want. With a good protocol, the code will be completely open-source, so users can be confident in the fairness and security of the system.
Generally speaking, cryptocurrencies allow anyone to participate in their development. New features or changes to code are reviewed by a community of developers before being approved and released. From there, users can review the code themselves and choose whether or not to run it.
Some updates will be backwards compatible, meaning updated nodes will still be able to communicate with older ones. Others will not be backwards compatible: nodes with the old version will be “kicked” from the network if they are not updated. See the article Hard forks and soft forks for an explanation on this.
Chapter 3 - How to invest in cryptocurrencies?
Contents
Which cryptocurrency should I buy?
What should I know before investing in cryptocurrencies?
Where to buy cryptocurrencies?
Centralized Exchanges (CEX)
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
Exchanges P2P
How to buy cryptocurrencies?
How to buy cryptos on Binance?
How to buy cryptos on the Binance DEX?
How to buy cryptos on Binance P2P?
Which cryptocurrency should I buy?
It's a choice that only you can make. You need to Do Your Own Research (DYOR) and decide based on your own analysis. That said, there are many tools that can help you make better decisions. For example, Binance Research provides excellent market analysis, as well as comprehensive reports on individual projects.
If you want to be able to evaluate which cryptocurrencies to buy right now, it is absolutely essential that you first understand how Bitcoin works. Good news, this is exactly why we created our guide What is Bitcoin? !
What should I know before investing in cryptocurrencies?
Where to start ? There are a multitude of ways to analyze financial markets and, in general, most professional investors use very different strategies. To summarize, however, there are two main schools of how to evaluate an investment: fundamental analysis (FA) and technical analysis (TA).
Fundamental analysis is a method for evaluating the valuation of an asset based primarily on economic and financial factors. Analysts who use this method study both macroeconomic and microeconomic factors, industry conditions, or the asset's underlying business (if applicable). In the case of cryptocurrencies, they can also examine public blockchain data, which are sometimes called on-chain metrics.
This can involve looking at transaction counts, addresses, top holders, network hash rate, and countless other pieces of information. The purpose of this analysis is to define a value for the asset and compare it to its current valuation. Ultimately, this approach aims to determine whether an asset is undervalued or overvalued.
That being said, it is important to remember that cryptocurrencies are a new and growing asset class. Fundamental analysis offers few tools to define the valuation of these new assets. Indeed, there is no standardized model for determining the value of digital assets, and the models that do exist are not reliable. The success or failure of a cryptocurrency project can depend on many different factors, which no current model can anticipate.
Technical analysts employ a different approach. Unlike fundamental analysts, technical analysts do not attempt to determine the intrinsic value of an asset. Instead, they look for trading or investment opportunities based on an asset's historical trading and valuation data. They do this by looking at price movements, chart patterns, indicators and other graphical tools to assess the strengths or weaknesses of a market. In essence, technical analysts believe that an asset's previous price movements can be useful in attempting to predict its future price movements.
Since technical analysis can be applied to any market using historical data, it is widely used by cryptocurrency traders.
So which approach should you learn? Well, why not both? Most market analysis tools work best when used in combination with other tools. In either case, it is absolutely vital to understand financial risk and risk management, and to never invest more than you can afford to lose.
Where to buy cryptocurrencies?
There are many ways to buy cryptocurrencies. The first thing to do is convert fiat funds into cryptocurrency. Then you can choose to HODL, trade against other cryptocurrencies or even lend them to earn interest. Let's take a look at the different types of cryptocurrency exchanges.
Centralized exchanges (CEX)
The concept of a centralized exchange can be confusing, as cryptocurrencies are often referred to as decentralized. In short, centralized exchanges are online platforms that facilitate trades by connecting buyers and sellers.
To make this work, users deposit their fiat and crypto assets on the exchange and trade them within the platform's internal systems. If you are familiar with how crypto wallets work, you will know that in this case the exchange keeps your funds. It should, however, be quite easy for you to withdraw your funds and keep them in your own wallet, if you wish.
Some prefer to keep their funds on the exchange, either because they trade regularly or for practical reasons. However, funds are at risk when the exchange is hacked.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
Decentralized exchanges are different. When you use a DEX, there is no custodian involved. In fact, a more accurate way to refer to this type of exchange would be no deposit exchange.
This is what happens when you trade on a DEX. Instead of depositing your funds into the exchange's wallet, you trade directly from your own wallet. When a trade is executed, funds are directly transferred via the blockchain thanks to the magic of smart contracts.
As there is no entity acting as a custodian, some consider this solution to be more secure than CEXs. Another advantage is that most DEXs do not require you to provide any personal information other than the blockchain wallet address. However, keeping your own funds requires some technical expertise, and you are entirely responsible for this.
Exchanges P2P
A peer-to-peer exchange (P2P) is also a place that connects buyers and sellers, but it is different from a CEX and a DEX. In this case, the exchange itself does nothing more than connect buyers and sellers, and they can settle the transaction however they want. So, the deposit and settlement method can be decided by buyers and sellers for each individual transaction.
How to buy cryptocurrencies?
How to buy cryptos on Binance?
Log in to Binance, or register if you don't have an account yet.
Go to the Buy and sell cryptocurrencies portal.
Select the cryptocurrency you wish to purchase and the currency you wish to pay with.
Select a payment method.
If prompted, insert your card details and complete the identity verification process.
It's over ! Your cryptocurrency will be credited to your Binance account.
How to buy cryptos on the Binance DEX?
Using a DEX is a bit more complicated than the other options available.
Here's what you need before you get started:
A wallet that can connect to Binance DEX (we recommend Trust Wallet).
A little BNB to pay transaction fees.
Once this is done, follow the instructions in our detailed Binance DEX guides:
Binance DEX: Interface Guide
Binance DEX: Creating a wallet
Binance DEX: Access your wallet
How to buy cryptos on Binance P2P?
Log in to Binance, or register if you don't have an account yet.
Go to the Binance P2P portal.
Select whether you want to buy or sell.
Filter by currency, payment method or other parameters that matter to you.
Select an ad that meets your needs or post your own.
Chapter 4 - Frequently asked questions about cryptocurrencies
Contents
Are cryptocurrencies legal?
Are cryptocurrencies dead?
Are cryptocurrencies safe?
Are cryptocurrencies anonymous?
Are cryptocurrencies valuable?
Are all digital currencies cryptocurrencies?
What is the capitalization of a cryptocurrency?
Why do I have to pay transaction fees?
I lost my key, can I recover my funds?
What is the future of cryptocurrencies?
Are cryptocurrencies legal?
Very few countries prohibit the purchase, sale or storage of cryptocurrencies. In the vast majority of the world, bitcoin and other virtual currencies are perfectly legal. But before you get started, you need to check if your jurisdiction allows it.
It is important to keep in mind that each country has a different approach to regulating cryptocurrency activities. Make sure you are not in violation of tax or compliance rules.
Are cryptocurrencies dead?

The media has pronounced the death of cryptocurrencies hundreds of times over the past decade. And yet, they continue to operate as they did in 2009. This does not mean that they are not volatile, their price fluctuates wildly. For those who are only trying to make a profit, bear markets can be very difficult to navigate.
However, it would be a mistake to declare cryptocurrencies “dead”. They continue to attract new users, and the technology and infrastructure only improves.
The fundamental innovations of Bitcoin and Ethereum will undoubtedly play an important role in reshaping our existing monetary systems so that they are better suited to current times. Immutability, resistance to censorship, use without trusted third parties, or near-instantaneous transactions using a public monetary system could completely shake up the mechanisms of economic activity on the Internet.
Are cryptocurrencies safe?
There is a certain degree of risk with cryptocurrencies. If you forget the password to access your bank account, simply have it reset by customer service. Be careful, if you forget or lose the private keys that give you access to your cryptocurrency, no one will be able to help you. Using a reputable exchange helps prevent certain errors, it requires trust, but you do not risk losing your private keys.
No hacker has yet been able to break public key cryptography. With good security measures, it's more likely that one of your other online accounts will be hacked than that your funds will be stolen. Best practices include knowing common scams (social engineering, phishing, etc.), taking your private keys offline permanently and saving them in a secure location.
Are cryptocurrencies anonymous?
Your name is not connected to your cryptocurrency addresses. They look like random strings of numbers and letters on the blockchain. Be careful, however, in assuming that this makes you anonymous. You are pseudonymous. You have some sort of identity on the blockchain, but it's not the one you use in real life.
There are some methods you can use to link IP addresses to your activities. At this point, smear attacks and other analysis techniques can be used to remove your anonymity. Remember that blockchains are essentially gigantic public databases. If you care about your privacy, you should make it as difficult as possible for others to link your transactions to your name. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin are not private by default, but methods such as bitcoin mixing and CoinJoins can make heuristic analysis unreliable.
A small subset of cryptocurrencies (called anonymous cryptocurrencies) are able to hide the source, destination, and amount of funds in transactions, using methods such as confidential transactions. They offer better privacy by default, but are not completely resistant to deanonymization.
Are cryptocurrencies valuable?
In essence, value is a shared belief. As with anything of value, value is not inherent in cryptocurrency itself, it is defined by people. In other words, something is valuable if people think it is. This is true whether the item of value is a precious metal, a piece of paper, or a few bits in a database.
That being said, some view cryptocurrencies and Bitcoin as rare digital commodities. Due to the predictability of its issuance rate and monetary policy, some argue that bitcoin could serve as a store of value in the future, like gold. With Bitcoin having only been around for a little over a decade, it remains to be seen whether it will stand the test of time in this regard.
Are all digital currencies cryptocurrencies?
No. You may have heard that many states and central banks are working on creating their own digital currencies. However, these are just digital currencies. In fact, they are often referred to collectively as central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). They are essentially digital versions of fiat currency, and they lack many of the benefits of cryptocurrencies. They are issued and declared as legal tender by a central government and generally do not use a distributed ledger, such as a blockchain, to keep a record of transactions.
You may also have heard of Facebook Libra, another type of digital currency. For Libra, it is planned to be built on an open-source blockchain system. However, it would not be permissionless like Bitcoin or Ethereum, meaning participants would need more than just an internet connection to use it. In addition, the project and its activity are managed by an association composed of a few selected members.
So although CBDCs and other forms of digital currency use blockchain or cryptography, they are very different from cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin.
What is the capitalization of a cryptocurrency?
When you look at the price of a cryptocurrency, you're only seeing the tip of the iceberg. An equally important measure is the number of individual units of this cryptocurrency, i.e. the supply.
Specifically, to assess the value of a cryptocurrency network, you need to know how many individual units exist at the moment. This is called circulating supply. Different cryptocurrencies may adopt different issuance strategies, so it is important to understand the issuance model adopted by each network.
Capitalization (or market capitalization) is the price of an individual unit multiplied by the circulating supply.
Market capitalization = Circulating supply * PriceAs you might imagine, the capitalization of a cryptocurrency network is a more accurate representation of the network's value than the price of an individual unit. A network whose unit is cheaper but whose circulating supply is greater may have a higher total valuation (capitalization) than a network whose each unit is more expensive but whose circulating supply is lower. And the opposite can also be true.
It should be noted, however, that capitalization does not represent the amount of money having entered a particular market. For example, newcomers often mistakenly think that Bitcoin capitalization represents the total amount of money invested in Bitcoin. But this doesn't make sense, because market capitalization depends on price and supply.
Why do I have to pay transaction fees?
If you send Bitcoin to another address, you will notice that the address receives a little less than you sent. In effect, you pay a small amount to compensate the miners who add your transaction to the blockchain.
Many cryptocurrencies use a similar mechanism to incentivize users to secure the network. In proof-of-work systems, transaction fees are typically bundled with freshly minted units (the block grant) to form the block reward.
You can adjust the fees based on the urgency of your transaction. Rational miners will always seek to generate as much revenue as possible, and will therefore prioritize transactions with higher fees. You can view current transactions to get an idea of average fees and set yours accordingly.
I lost my key, can I recover my funds?
If you're sure you've lost your keys, there's a good chance you'll never find them again. The great advantage of cryptocurrencies is to remove custodians and intermediaries from the management of financial transactions. The downside, however, is that the responsibility is now entirely in your hands. You must therefore be extremely careful not to lose your private keys, as they give you ownership of your funds.
What is the future of cryptocurrencies?
The future of cryptocurrencies depends entirely on the opinion of the person you ask. Some believe that Bitcoin will replace gold in the digital age and disrupt the existing financial system. Others argue that cryptocurrencies will always be a secondary system, existing as a niche market. We also have those who believe that Ethereum will become a distributed computer, serving as the basis for a new Internet.
Skeptics predict the industry will eventually collapse, while enthusiasts are content to see cryptocurrencies remain niche monetary systems. There are many possible outcomes: it's simply too early to say with certainty what will happen even a year from today. But we cannot deny that there is enormous growth potential.






