What is trade?
Trade is a fundamental concept of economics that involves the buying and selling of valuables. These may be goods and services for which the buyer pays the seller some compensation. In other cases, trade may involve the exchange of goods and services between parties to a transaction.
In the context of financial markets, the assets traded are called financial instruments. These can be stocks, bonds, Forex currency pairs, options, futures, margin products, cryptocurrencies and other instruments. If you're not familiar with any of the terms on this list, that's okay—we'll explain them throughout the article.
The term "trading" is generally used to refer to short-term trading, where traders actively open and close positions over relatively short periods of time. However, this definition is somewhat misleading. In fact, trading can refer to a wide range of different strategies such as day trading, swing trading, trend trading, etc. But don't worry. We'll look at these strategies in more detail later.
Do you want to put the acquired knowledge into practice?
What is investing?
Investing is the investment of resources (such as capital) with the expectation of making a profit. This includes using money to finance and start a business or buying land with the intention of resale at a higher price. In the context of financial markets, it usually refers to investing in financial instruments with the expectation of selling them later at a higher price.
A key concept in investing is return on investment (also known as ROI). Unlike trading, investing takes a longer-term approach to building wealth. The goal of an investor is to accumulate wealth over a long period of time (years or even decades). There are many ways to do this, but usually the search for potentially good investment opportunities starts with the fundamentals.
The long-term nature of the strategy allows investors not to worry about temporary price fluctuations. As a rule, they behave relatively passively and do not pay much attention to short-term losses.
Trading and investing - what's the difference?
Both traders and investors strive to make a profit in financial markets. However, their methods of achieving this goal are different.
Typically, investors want to make profits over a longer period of time - remember what we said about years and even decades. And because investors have a longer time horizon, their target return for each investment tends to be larger, too.
On the other hand, traders try to benefit from market volatility. They open and close positions more often and allow lower returns on each trade (as they often open several at once).
Which strategy is better? Which one is more acceptable for you? You decide. You can start by studying the markets and then start practicing. Over time, you will learn to determine which strategy is best for your financial goals, personality, and trading profile.
Remember how the price of Bitcoin (BTC) has changed recently.
What is fundamental analysis (FA)?
Fundamental analysis is a method for estimating the value of a financial asset. A fundamental analyst studies economic and financial factors to determine whether an asset is fairly valued. Fundamental analysis looks at macroeconomic circumstances, such as the state of the overall economy, industry conditions, and the business associated with the asset (if any). Often these circumstances are monitored using leading and lagging macroeconomic indicators.
Based on the results of fundamental analysis, the analyst must determine whether the asset is undervalued or overvalued. Investors can use the findings when making investment decisions.
In the case of cryptocurrencies, fundamental analysis can also be based on Data Science, which processes publicly available blockchain data called on-chain metrics. These metrics include: network hashrate, holder rating, number of addresses, transaction analysis and much more. Using the wealth of public blockchain data available, analysts can create sophisticated technical indicators that measure specific aspects of the overall health of the network.
Although fundamental analysis is widely used in the stock market or forex market, it is less suitable for analyzing the cryptocurrency market as it stands today. This asset class is so new that there is simply no standardized, comprehensive framework for determining market valuation yet. Moreover, market movements are predominantly influenced by speculation and narratives. Thus, fundamental factors have little impact on cryptocurrency prices. However, as the market matures, more accurate ways of estimating the value of crypto assets may be developed.
What is technical analysis (TA)?
Technical analysts take a different approach. The basic idea of technical analysis is that historical price behavior can indicate likely future market movements.
Technical analysts do not seek to find out the actual value of an asset. Instead, they look at historical trading activity and try to identify trading opportunities based on that. Technical analysis includes metrics such as price movement and volume, chart patterns, the use of technical indicators, and many other charting tools. The purpose of this analysis is to assess the strength or weakness of a given market.
With that said, technical analysis is not only a tool for predicting likely future price movements. It can also be a useful risk management framework. Because technical analysis provides a model for analyzing market structure, it makes trade management more specific and measurable. In this context, measuring risks is the first step to managing them. This is why some technical analysts cannot be considered traders in the narrow sense. They may use technical analysis solely as a risk management tool.
The practice of technical analysis is applicable to any financial market and is widely used by cryptocurrency traders. But what is the secret of its effectiveness? As we have already said, the valuation of cryptocurrency markets is subject to speculation. This makes them an ideal platform for technical analysts as they can benefit by only considering technical factors.
Fundamental analysis and technical analysis – which is better?
It completely depends on your trading strategy. In fact, why not use both methods? Most market analysis methods work best in combination with other methods or indicators. Thus, there is a greater chance of discovering more reliable investment opportunities. Combining different trading strategies can also help eliminate bias in the decision-making process.
This approach is sometimes called merging. Confluence traders combine several strategies, taking advantage of the strengths of each. The idea is that the trading opportunities provided by combined strategies can be stronger than those provided by just one strategy.
Thinking about where to start working with cryptocurrencies? Buy Bitcoin on Binance!
What influences financial markets?
The price of an asset is determined simply by the balance of supply and demand. In other words, it is determined by buyers and sellers. Where supply meets demand, a market appears. But what else can increase the value of a financial asset?
We have already said that the reason may be fundamental factors (for example, the state of the economy); technical factors (such as cryptocurrency market capitalization); as well as other factors that should be taken into account (for example, market sentiment or recent news).
However, all these are just additional “variables”. In reality, the price of an asset at a particular moment is determined by the balance of supply and demand.
What is a market trend?
A trend is the general direction of market movement. In technical analysis, market trends are determined using price movements, trend lines, or even key moving averages.
There are two main market trends - bullish and bearish. A bull market means a sustained uptrend in which prices are constantly rising. A bear market refers to a sustained downward trend in which prices are constantly declining. Consolidating, or “sideways”, markets without a clearly directed trend are also distinguished.

Bitcoin remained in a bull market throughout its existence.
Note that a market trend does not mean that the price always moves in the direction of the trend. In a prolonged bull market, there may be short-term bearish trends and vice versa. This is the nature of market trends. You could say it's a matter of perspective because it all depends on the time frame you're looking at. In the context of long time frames, market will always matter more than in the context of short time frames.
The peculiarity of market trends is that they can only be determined with absolute certainty in hindsight. You may have heard of the concept of hindsight bias, where people tend to convince themselves that they accurately predicted an event before it happened. As you can imagine, hindsight bias can have a significant impact on identifying market trends and making trading decisions.
What is the market cycle?
You may have heard the expression “the market is cyclical.” A cycle is a pattern or trend that occurs at different periods. Generally, market cycles on higher time frames are more reliable than on lower ones. But even on an hourly chart, you can find small market cycles – just as you can when looking at decades of data.
Markets are cyclical by nature. Cycles can cause certain asset classes to outperform others. At other points in the same market cycle, the same asset classes may underperform other classes due to different market conditions.
It is worth noting that at any given moment it is impossible to understand exactly what stage of the market cycle we are at. Analysis can only be performed with high accuracy after part of the cycle has been completed. Market cycles also rarely have a specific beginning and end, which means being “here and now” in the context of financial markets is a highly biased point of view.
If you want to learn more about market cycles, read our article “The Psychology of Market Cycles.”
Ready to try trading on a crypto exchange?
Chapter 2 – Financial markets and trading instruments
Content
What is a financial instrument?
What is the spot market?
What is margin trading?
What is the derivatives market?
What are forward and futures contracts?
What are perpetual futures contracts?
What are options?
What is the Forex market?
What are Binance Leveraged Tokens?
What is a financial instrument?
In simple words, a financial instrument is a tradable asset. For example, cash, precious metals (gold or silver), documents confirming ownership of something (such as a business or resource), the right to transfer or receive cash, and much more. Financial instruments may be truly complex, but their essence remains the same: whatever they are and whatever they mean, they can be traded.
Depending on the classification, different types of financial instruments are distinguished. One of the classifications is based on determining what kind of instruments they are: basic or derivative. As the name suggests, derivatives derive their value from something else (such as cryptocurrency). Financial instruments can also be classified as debt or equity.
But what are cryptocurrencies? We may perceive them differently, and they may fall into more than one category. The easiest way would be to classify them as a digital asset. However, the potential of cryptocurrencies lies in the formation of a completely new financial and economic system.
In this sense, cryptocurrencies form a fundamentally new category of digital assets. Moreover, as the ecosystem develops, many new categories may emerge that would otherwise never have appeared. The first such examples can be seen in the field of decentralized finance (DeFi).
What is the spot market?
In the spot market, financial instruments are traded for so-called “immediate delivery”. Delivery in this context simply means the exchange of a financial instrument for money. This may not seem like a significant difference, but in some markets cash payments are not instantaneous. For example, if we are talking about the futures market, assets are delivered on a specific date in the future (when the futures contract expires).
Simply put, the spot market can be perceived as a kind of space where transactions are made “on the spot”. Because trades are settled immediately, the current market price of an asset is often called the spot price.
What does this mean in the context of cryptocurrency markets? What can you do on the Binance Spot Market? You can exchange some coins for others. That is, if you want to exchange BNB for BUSD, then you simply go to the BNB/BUSD spot market and make a trade! Likewise, if you want to exchange BNB for BTC, then you go to the BNB/BTC spot market. Once your orders are filled, coins will be exchanged immediately. And this is one of the easiest ways to trade cryptocurrencies.
What is margin trading?
Margin trading is a method of trading using borrowed funds from a third party. In fact, margin trading increases results - both positively and negatively. A margin account gives traders greater access to capital and eliminates some counterparty risk. How? The idea is that traders can trade with the same position size, but keep less capital on the cryptocurrency exchange.
When talking about margin trading, the terms “margin” and “leverage” often appear. Margin refers to the amount of capital you contribute (i.e. your own resources). Leverage means the ratio by which you increase your margin. For example, if you use 2x leverage, this means you are opening a position that is double the size of your margin. If you use 4x leverage, then the open position is four times the margin, and so on.
However, be wary of liquidation. The more leverage you use, the closer the liquidation price is to the entry price. If you are liquidated, you will lose all your margin. So, when starting margin trading, be aware of the high risks associated with it. And before you get started, we strongly recommend that you read the article “Guide to Margin Trading on Binance”.
Margin trading is widely used in trading stocks, commodities and Forex, as well as in the Bitcoin and cryptocurrency markets. In a more traditional setting, borrowed funds are provided by an investment broker. When it comes to cryptocurrencies, funds are usually provided by an exchange, which charges a funding fee. However, in some cases, borrowed funds may come directly from other traders on the platform. Typically, this method involves a variable interest rate (finance fee) as it is determined in the open market.
So, we have briefly reviewed the concept of margin trading, but you can always expand your knowledge. If you are interested in learning more, read our article “What is Margin Trading?”
What is the derivatives market?
Derivatives are financial assets whose value is based on some other asset. This could be an underlying asset or a basket of assets. The most common underlying assets are stocks, bonds, commodities, market indices or cryptocurrencies.
A derivative itself is a contract between several parties. It derives its price from the underlying asset that is used as input. Whatever asset is used as a benchmark, the basic idea is that the derivative product derives its value from it. Common examples of derivatives are futures contracts, options contracts and swaps.
According to some estimates, the derivatives market is one of the largest. Why? Derivatives can exist for almost any financial product, even derivatives themselves. Yes, yes, derivatives can be created on the basis of derivatives. Then, based on these derivatives, others can be created - and so on. Reminds me of a very unstable house of cards, doesn't it? And this is not too far from the truth. It is believed that the derivatives market played a major role in the 2008 financial crisis.
What are forward and futures contracts?
A futures contract is a type of derivative product that allows traders to speculate on the future price of an asset. This refers to an agreement between the parties to complete a transaction at a later date, called the expiration date. As with derivatives, the underlying asset for such a contract can be any asset. The most common examples are cryptocurrencies, commodities, stocks and bonds.
The expiration date of a futures contract is the last day on which a specific contract is traded. At the end of that day, the contract expires at the last traded price. The type of performance under the contract is determined in advance and can be either settlement or delivery.
With physical delivery, the underlying asset of the contract is exchanged directly. For example, barrels of oil are delivered. In cash settlement, the underlying asset is not directly exchanged, only the value represented (in the form of money or cryptocurrency) is exchanged.
If you want to trade futures on Binance, be sure to check out the Advanced Guide to Trading on Binance Futures.
What are perpetual futures contracts?
Futures products are a convenient way for traders to speculate on the price of an asset. But what if they want to hold the position even after the futures expire?
For this purpose, perpetual futures contracts were created. The main difference between them and regular futures contracts is that they do not have an expiration date. This way, traders can speculate on the price of the underlying asset without worrying about expiration.
However, this creates another problem. What if the price of a perpetual futures contract becomes very far from the price of the underlying asset? Because there is no expiration date, there may be a persistent discrepancy between the price in the perpetual futures market and the price in the spot market.
This is why there is a funding fee for perpetual futures contracts between traders. Let's imagine that the perpetual futures market is trading higher than the spot market. In this case, the funding rate is positive, meaning long positions (buyers) pay a funding fee to short positions (sellers). This motivates buyers to sell, causing the contract price to fall, bringing it closer to the spot price. Conversely, if the perpetual futures market is trading lower than the spot market, the funding rate is negative. In this case, short positions pay long positions to encourage the contract price to rise.
To summarize, with positive financing, the longs pay the shorts. If funding is negative, the shorts pay the longs.
Perpetual futures contracts are very popular among traders of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. If you want to learn more about perpetual futures contracts, read the article "What are perpetual futures contracts?"
Do you want to create your own investment portfolio?
What are options?
An options contract is a derivative financial instrument that gives traders the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell an asset at a specific price in the future. The main difference between a futures contract and an options contract is that options contracts do not have to be settled.
When traders buy an options contract, they are speculating on price changes.
There are two types of options contracts: call and put options. A call bets that the price will go up, while a put bets that the price will go down.
As with other derivatives, options contracts can be based on a variety of financial assets: market indices, commodities, stocks, cryptocurrencies, etc.
Options contracts can involve very complex trading strategies and risk management techniques such as hedging. In the context of cryptocurrencies, options can be especially useful for miners looking to hedge their significant cryptocurrency holdings. This way, they are better protected from events that could negatively impact the value of their funds.
If you want to learn more about options contracts, read the article “What are Options Contracts?” If you want to trade options on Binance, be sure to read our Options Guide for iOS and Android first.
What is the Forex market?
In the foreign exchange market (Forex, FX), traders can exchange the currency of one country for the currency of another. Essentially, the Forex market determines currency exchange rates for the entire world.
We often think of currencies as a “safe haven” among assets. Even the term “stablecoin” means that in theory the asset is somehow protected from volatility. This is partly true. However, currencies can also experience significant fluctuations in the market. Why? The value of currencies is also determined by supply and demand. In addition, they may be affected by inflation or other market forces associated with global trade and investment, as well as geopolitical factors.
How does the Forex market work? Currency pairs can be traded by investment banks, central banks, commercial companies, investment firms, hedge funds and retail Forex traders. The Forex market also allows you to convert global currencies for international trade settlements.
To increase their profits, Forex traders typically use day trading strategies such as leveraged scalping. What this means, we will look at here a little later.
The Forex market is one of the main building blocks of the modern global economy as we know it. In fact, the Forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world.
What are Binance Leveraged Tokens?
Leveraged tokens are tradable assets that provide a multiplier of exposure to cryptocurrency without the usual requirements of managing such a position. This means you don't have to worry about margins, collateral, financing or liquidation.
Leveraged tokens are an innovative financial product that exists only thanks to the capabilities of the blockchain. Leveraged tokens were originally introduced by the derivatives exchange FTX, and various alternative implementations have since emerged. However, the basic idea remains the same: tokenization of open positions with leverage. What does it mean?
Leveraged tokens represent open perpetual futures positions in tokenized form. Remember when we said that derivatives can be created on the basis of derivatives? Leveraged tokens are a prime example of complex derivatives because they derive their value from futures positions, which are also derivatives.
Leveraged tokens are a great way to gain access to more cryptocurrency. If you are looking to trade Leveraged Tokens on Binance, check out the Beginner's Guide to Binance Leveraged Tokens (BLVT).
If you want to learn more about FTX Leveraged Tokens, check out the Beginner's Guide to FTX Leveraged Tokens.
Chapter 3 – Trading and Investment Strategies
Content
What is a trading strategy?
What is portfolio management?
What is risk management?
What is day trading?
What is swing trading?
What is position trading?
What is scalping?
What is diversification and asset allocation?
What is Dow Theory?
What is Elliott wave theory?
What is the Wyckoff method?
What is a buy and hold strategy?
What is investing?
What is demonstration trading?
What is a trading strategy?
A trading strategy is simply a plan that you follow when making trades. There is no one right approach to trading, so each strategy will largely depend on the profile and preferences of the trader.
Regardless of your approach to trading, developing a plan is critical. It sets clear goals and keeps you from getting carried away by emotions. When making a plan, you must decide what you are going to trade, how you are going to do it, and at what points you are going to enter and exit.
In this chapter, we will look at several popular trading strategies.
What is portfolio management?
Portfolio management involves constructing and managing a portfolio of investments. The portfolio itself is a group of assets - anything from Beanie Babies to real estate. If you trade cryptocurrencies exclusively, then your portfolio likely includes Bitcoin and other digital coins and tokens in some proportion.
Your first step: define your portfolio expectations. Are you interested in a basket of investments that is relatively sheltered from volatility, or something riskier that could provide higher returns in the short term?
It's useful to think about how you want to manage your portfolio. Someone may choose a passive strategy - distribute investments among assets and not touch them again. Others will take an active approach, where they must continually buy and sell assets to make a profit.
What is risk management?

Risk management is paramount to success in trading. It starts with identifying the types of risks you may face.
Market risk: The loss you may suffer if an asset loses value.
Liquidity risk: Potential losses that arise in illiquid markets where it may be difficult to find buyers for certain assets.
Operational risk: potential losses arising from operational failures. They may be due to human error, hardware/software failure, or intentional fraud on the part of employees.
Systemic risk: potential losses caused by failures of players in the industry in which you invest, which affects all companies in that sector. For example, in 2008, the collapse of Lehman Brothers caused a cascading effect in global financial systems.
As you can see, risk identification begins with an audit of the assets in your portfolio. But for it to be effective, it is necessary to take into account both internal and external factors. These risks should then be assessed. How often do you encounter them? How serious are they?
By weighing the risks and understanding their potential impact on your portfolio, you can rank them and develop appropriate strategies and responses. For example, systemic risk can be reduced through diversification into different assets, and market risk through stop losses.
Be sure to check out our Financial Risk and Beginner's Guide to Risk Management resources.
What is day trading?
Day trading, or day trading, is a strategy that involves entering and exiting positions within one day. The term originated from traditional markets, given that they are only open for a certain period of time during the day. There should be no open positions outside of these periods.
Cryptocurrency markets, as you probably know, are always open. You can trade 24 hours a day, every day of the year. Therefore, in the context of cryptocurrencies, day trading refers to a style of trading in which a trader enters positions and closes them within 24 hours.
Technical analysis is often used to determine which assets to day trade. Since profits over such a short period are usually minimal, you can trade a wider range of assets to try to increase them. However, some may trade exclusively in the same pair for years.
Obviously, this style is a very active trading strategy. It can be highly profitable, but it also carries significant risk. Thus, day trading is mainly suitable for experienced traders.
Thinking about where to start working with cryptocurrencies? Buy Bitcoin on Binance!
What is swing trading?
With swing trading, you are also trying to profit from market trends, but the time horizon is longer: positions are usually held from a couple of days to a couple of months.
Your goal is to find an asset that looks undervalued and has the potential to rise in value. You could then buy the asset and then sell it when its price rises to make a profit. Or you can try to find overvalued assets that are about to fall in value. You can then sell some of them at a high price with the expectation of buying them again at a low price.
Like day traders, many swing traders turn to technical analysis. But since their strategy covers a longer period, fundamental analysis may also be relevant.
Swing trading is considered a more beginner-friendly strategy. It is much less stressful than the fast-paced day trading. If the latter is characterized by quick decision-making and the need to constantly monitor the situation on the market, you can take your time in swing trading.
What is position trading?
Positional (or trend) trading is a long-term strategy. Traders buy assets and hold them for a long period (on the order of several months). Their goal is to profit from the future sale of assets at a higher price.
What distinguishes position trades from long-term swing trades is the rationale behind their placement. Position traders are interested in long-term trends: they try to profit from the overall direction of the market. On the other hand, swing traders seek to predict "swings" in the market that do not necessarily correlate with the broader trend.
It is not surprising that position traders prefer fundamental analysis simply because their time horizon allows them to monitor long-term processes. This does not mean that technical analysis is not used at all. While position traders expect a trend to continue, the use of technical indicators can alert them to the possibility of a reversal.
Like swing trading, position trading is an ideal strategy for beginners. Again, a longer time horizon leaves more room to think about your decisions.
What is scalping?
Of all the strategies under consideration, scalping operates with the shortest time intervals. Scalpers try to catch small price movements by often entering and exiting positions within a matter of minutes (or even seconds). In most cases, they use technical analysis to predict price movements, monitor bid-ask spreads and other imperfections to make a profit. Due to the short time periods, scalping trades typically yield a small percentage of profits: less than 1%. But scalping is a numbers game, so repeating small profits can add up over time.
Scalping is not a strategy for beginners. To be successful, you must have a deep understanding of the markets, the platforms you trade on, and technical analysis. However, for traders who know exactly what they are doing, identifying the right patterns and taking advantage of short-term fluctuations can be very profitable.
What is diversification and asset allocation?
The terms "allocation" and "diversification" are usually used interchangeably. You probably know the expression “don’t put all your eggs in one basket.” Keeping all your eggs in one basket creates a single point of failure—and that includes your assets. Investing your entire savings in one asset exposes you to similar risk. If you invested in the stock of one particular company and that company went bankrupt, you would lose all your funds overnight.
Note that this is true not only for individual assets, but also for asset classes. In the event of a financial crisis, be prepared for all your shares to lose value. This is because they are highly correlated in the sense that they tend to follow the same trend.
Good diversification isn't just about filling your portfolio with hundreds of different digital currencies. Suppose world governments ban cryptocurrencies or quantum computers disrupt the public key cryptography schemes used in cryptocurrencies. Any of these events will have a major impact on all digital assets. They, like shares, constitute a single asset class.
Ideally, the investment should be spread across several classes. This way, if any asset has a problem, the rest of your portfolio won't be affected. Nobel laureate Harry Markowitz presented this idea in the form of modern portfolio theory (MPT, or Modern Portfolio Theory). The theory makes the case for reducing volatility and risk associated with portfolio investments by using non-correlated assets.
If you are interested in this topic, read the Binance Academy article “Asset Allocation and Diversification” and the Binance Research article “Exploring the Benefits of Diversification with Bitcoin.”
What is Dow Theory?

The Dow Theory is financial principles modeled on the ideas of Charles Dow. Dow founded the Wall Street Journal and helped create the first US stock indices, also known as the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) and the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA).
Although Dow's theory was never formalized by himself, it can be viewed as a set of market principles presented in his works. Here are some key findings:
Everything is reflected in the price. Dow was a proponent of the efficient market hypothesis (EMH), the idea that markets reflect all available information about asset prices.
There are market trends. The Dow is often credited with the very concept of market trends as we know them today, distinguishing between primary, secondary and tertiary trends.
There are three phases of the primary trend. In primary trends, Dow identified the accumulation phase, the participation phase, and the revaluation and distribution phase.
Cross-index correlation. Dow believed that a trend within one index could not be confirmed unless it was observed in another index.
Volume is important. The trend is also confirmed by high trading volume.
Trends are valid until they reverse. If the trend is confirmed, it continues until there is a clear reversal.
Of course, a caveat should be made that this is not an exact science, but a theory that may not correspond to reality. However, this theory remains influential, and many traders and investors consider it an integral part of their methodology.
If you want to learn more, read the article "Introduction to Dow Theory".
What is Elliott wave theory?
Elliott Wave Theory (EWT) is the principle that market movements follow the psychology of market participants. Although the theory is used in many technical analysis strategies, it is not an indicator or a specific trading technique. It is rather a way of analyzing market structure.
The Elliott wave pattern is usually defined as a series of eight waves, each of which is either impulsive or corrective. Five of these waves are impulse, that is, following the general trend, and three are corrective, that is, moving against the trend.

Elliott wave cycle with impulse waves (blue) and corrective waves (yellow).
The patterns also have a fractal property - you can zoom in on one wave and see another Elliott pattern on a smaller scale. Conversely, you may zoom out and discover that the pattern you are examining is also one wave of a larger Elliott Wave cycle.
Elliott wave theory has received mixed reviews. Some argue that the methodology is too subjective because traders can identify waves in different ways within the rules. Like the Dow Theory, Elliott Wave Theory is not reliable and should not be considered an exact science. However, many traders have had great success using EWT in combination with other technical analysis tools.
If you want to learn more, read the article "Introduction to Elliott Wave Theory".
What is the Wyckoff method?
The Wyckoff Method is a broad-based trading and investment strategy developed by Charles Wyckoff in the 1930s. His work is considered a cornerstone in the development of modern technical analysis techniques in many financial markets.
Wyckoff proposed three fundamental laws: the law of supply and demand, the law of cause and effect, and the law of effort and result. He also formulated the theory of the "composite man", which in many ways echoes the phases of the primary trends of Charles Dow. His work in this area is especially valuable for cryptocurrency traders.
In practical terms, the Wyckoff Method is a five-step approach to trading. It can be divided into the following stages:
defining a trend: what it is and where it is moving;
determining the strength of an asset: whether it moves with the market or in the opposite direction;
identifying an asset with growth potential: whether there are enough reasons to enter the position and whether the risk is worth the potential income;
assessment of the probability of growth: do analysis indicators indicate a possible movement - for example, Wyckoff tests for buying and selling an asset; what is the volume of supply and demand; is the asset ready to move;
determination of entry time: what is the position of the asset in relation to the general market; what is the best time to enter a position.
The Wyckoff method appeared almost a century ago, but remains relevant today. The scope of Wyckoff's research is extremely large, so the above abstracts should be considered a very condensed overview. We recommend studying his works in more depth, as they are a source of extremely important knowledge in the field of technical analysis. You can start with the article “The Wyckoff Method”.
What is a buy and hold strategy?
The buy and hold strategy, as the name suggests, involves buying and holding an asset. This is a long-term passive strategy in which investors buy an asset and then hold it regardless of market conditions. A good example in the crypto space is hodling, practiced by those investors who prefer to buy and hold for many years instead of actively trading.
This strategy can be beneficial for those who choose to invest independently because there is no need to worry about short-term fluctuations or capital gains taxes. On the other hand, it requires the investor to be patient and hold on. on the assumption that the asset will not depreciate.
If you want to learn a simple way to apply this strategy to Bitcoin, read the article “What is Dollar Cost Averaging (DCA)?”
What is investing?
Index investing can be considered a variant of the buy and hold strategy. As the name suggests, an investor seeks to profit from the movement of assets within a specific index. This is done by purchasing assets yourself or investing in an index fund.
Again, this is a passive strategy. Individuals can also benefit from diversification across multiple assets without the stress of active trading.
What is demonstration trading?
Paper trading can be carried out in accordance with any strategy, the point is that the trader only simulates the purchase and sale of assets. This is especially useful for beginners (as well as experienced traders) to test their skills without risking money.
For example, let's say you've discovered a good strategy for timing Bitcoin drops, and you now want to try to profit from those drops before they actually happen. Before you risk everything, you can test your strategy through paper trading. This can be as simple as recording the price at the time you "opened" your short and at the time you closed the position. Additionally, you can use simulators that simulate popular trading interfaces.
The main advantage of paper trading is that you can test strategies without losing money if something goes wrong. This is the ability to emulate actions with zero risk. Of course, you need to understand that paper trading only gives you a limited view of the real environment. It's hard to replicate the real emotions you feel when it comes to money. Paper trading without a real simulator can also be misleading about trading-related costs and commissions if you don't factor them into specific platforms.
Binance offers a variety of paper trading options. For example, the Binance Futures testnet provides a full interface. If you are creating trading bots or programs, you can access the spot exchange testnet through the API.
Chapter 4 – Basics of Technical Analysis
Content
What is a long position?
What is shortening?
What is an order book?
What is order book depth?
What is a market order?
What is slippage in trading?
What is a limit order?
What is a stop loss order?
Who are makers and takers?
What is a bid-ask spread?
What are candlestick charts?
What are candlestick charts?
What is a trend line?
What is support and resistance?
What is a long position?
A long position (or simply long) means buying an asset in anticipation of its price rising. Long positions are often used in the context of derivatives or Forex, but the concept applies to almost any asset class or market type. Buying an asset on the spot market in the hope that its price will rise can also be classified as opening a long position.
Going long on a financial product is the most common way of investing, especially for beginners. Long-term trading strategies such as buy and hold are based on the assumption that the underlying asset will rise in value. In this sense, using a buy and hold strategy is simply being long for an extended period of time.
However, going long does not necessarily mean that the trader expects to benefit from an upward price movement. Let's take leveraged tokens as an example. BTCDOWN is inversely proportional to the price of Bitcoin. If the price of Bitcoin increases, then the price of BTCDOWN decreases. If the price of Bitcoin decreases, the price of BTCDOWN increases. In this sense, opening a long position on BTCDOWN is equivalent to lowering the price of Bitcoin.
What is shortening?
A short position (or short) means selling an asset with the intention of buying it back later at a lower price. Shorting is closely related to margin trading because it can operate with borrowed assets. However, it is also widely used in the derivatives market and can be implemented using a simple spot position. So how does shorting work?
When it comes to shorting on spot markets, it is quite simple. Let's say you have Bitcoin and you expect its price to go down. You sell BTC for USD, hoping to buy it later at a lower price. In this case, when you sell at a high price and plan to buy back at a low price, you are entering a short position in Bitcoin. Simple enough. But how does leveraged shorting work? Let's consider.
You borrow an asset that you believe will decline in value, such as a stock or cryptocurrency. You sell it immediately. If the market moves in your favor and the price of the asset declines, you buy back the same amount of the asset that you borrowed. You repay the loan (with interest) and make a profit from the difference between the price at which you originally sold and the price at which you bought again.
What does leveraged shorting of Bitcoin look like? Let's consider this example. We provide the necessary collateral to borrow 1 BTC and then immediately sell it for $10,000. We received $10,000. Let's say the price drops to $8,000. We buy 1 BTC and pay off the debt in the amount of 1 BTC with interest. Since we originally sold Bitcoin for $10,000 and now bought it back for $8,000, our profit is $2,000 (less interest and trading fees).
What is an order book?
An order book (order book, stock book) is a collection of current open transactions for an asset, ordered by price. If you post an order that is not filled immediately, it is added to the order book. It will remain there until it is filled with another order or cancelled.
Order books on each platform are different, but generally contain approximately the same information. They display the number of orders at certain price levels.
In the case of cryptocurrency exchanges and online trading, orders in the order book are matched by a system called a matching engine. This system ensures the execution of transactions. Consider it a kind of brain of the exchange. Along with the order book, this system forms the basis of the electronic exchange concept.
What is order book depth?
Order book depth (or market depth) refers to the visualization of currently open orders in the order book. The chart shows a set of buy orders and a set of sell orders from different sides.
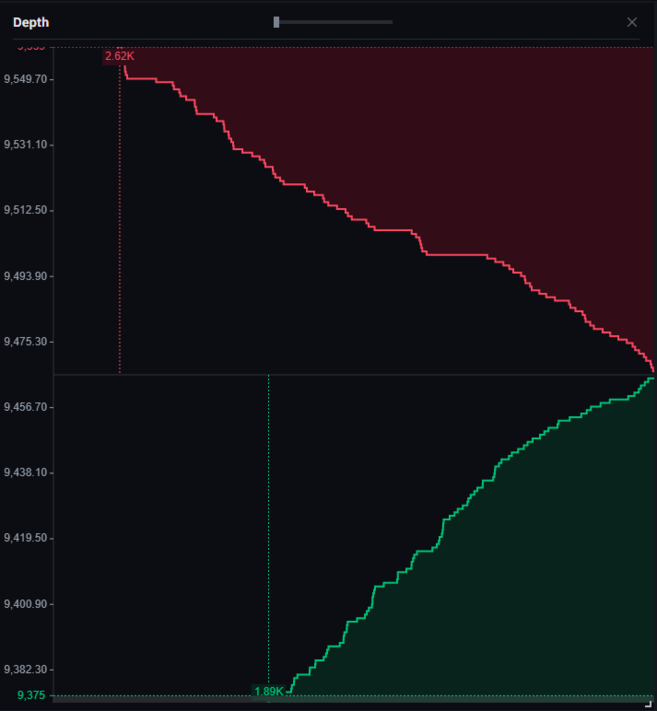
Order book depth of the BTC/USDT market pair on Binance.
More generally, order book depth refers to the amount of liquidity that an order book can realize. The “deeper” the market, the more liquidity there is in the order book. In this regard, a market with greater liquidity can close larger orders without significantly affecting the price. But if the market is illiquid, large orders can significantly affect the price.
What is a market order?
A market order is an order to buy or sell at the best market price available at that time. Essentially, this is the fastest way to enter and exit the market.
When you open a market order, you are essentially saying, “I want to fill this order right now at the best price I can get.”
Your market order will fill orders from the order book until it is completely filled. This is why large traders (or whales) can have a significant impact on price when they use market orders. A large market order can effectively siphon liquidity from the order book. How does this happen? Let's look at this when discussing slippage.
Want to know more? Read the article “What is a market order?”
What is slippage in trading?
When using market orders, it is important to keep slippage in mind. When we say market orders are filled at the best available price, this means that they fill orders from the order book until the entire order is filled.
But what if there is not enough liquidity at the desired price to fill a large market order? In this case, there may be a large difference between the execution price you expected and the actual price. The difference between them is called slippage.
Let's say you want to go long 10 BTC on an altcoin. However, this altcoin has a relatively small market capitalization and trades in a market with low liquidity. If you use a market order, it will continue to fill orders from the order book until the entire 10 BTC order is filled. In a liquid market, you will be able to fill an order for 10 BTC without significantly affecting the price. In this case, the lack of liquidity means that the order book may not have enough sell orders in the current price range.
So, by the time the entire 10 BTC order is filled, you may find that the average price is much higher than expected. In other words, not enough sell orders resulted in your market order being matched with orders that were priced significantly higher than the initial price.
Always be aware of slippage when trading altcoins - some trading pairs may not have enough liquidity to fill your market orders.
What is a limit order?
A limit order is an order to buy or sell an asset at a specific price or higher. This price is called the limit price. Buy limit orders are executed at or below the limit price, and sell limit orders are executed at or above the limit price.
When you open a limit order, you are essentially saying, “I want to fill the order at a specific price or higher, but not lower.”
Using a limit order allows you to have greater control over your entry and exit points for a specific market. It guarantees that your order will never be fulfilled at a price worse than your desired one. However, there is a downside to this. The market may never reach your price, leaving the order unfilled. In many cases, this means a lost trading opportunity.
The choice in favor of a limit or market order is individual for each trader. Some traders may use only one or only the second, while others will use both - depending on the circumstances. So that you can make the right decision for yourself at the right time, you need to understand how they work.
Want to know more? Read the article “What is a limit order?”
What is a stop loss order?
Now that we know what market and limit orders are, let's talk about stop loss orders. A stop loss order is a type of limit or market order that is only activated when a certain price is reached. This price is called a stop price.
The main purpose of a stop loss is to limit losses. Every trade must have a cancellation point - a price level that you must determine in advance. This is exactly the level at which you say that your previous actions were wrong and you should exit the market to prevent further losses. So the cancellation point is the level at which you place your stop loss.
How does a stop loss order work? We have already said that stop loss can be either limit or market. This is why variations include stop-limit and stop-market orders. The key feature is that the stop loss order is only activated when a predetermined price (stop price) is reached. When the stop price is reached, the order becomes a market or limit order. That is, you set a stop price as a trigger for posting a market or limit order.
But there is one thing to remember. Limit orders are executed only if the current price of the asset is equal to or higher than the limit price. At a lower price, execution does not occur. If you use a stop-limit order as a stop-loss order, then if the market falls sharply, the price can instantly break through the set limit price, leaving your order unfilled. In other words, the stop price of the order will be triggered, but it will remain unfilled due to a sharp drop in price. This is why stop market orders are considered safer than stop limit orders. They ensure that even in extreme market conditions, you will sell assets and close the position as soon as the set price point is reached.
Want to know more? Read the article “What is a stop-limit order?”
Thinking about where to start working with cryptocurrencies? Buy Bitcoin on Binance!
Who are makers and takers?
You become a maker when you post an order that is not filled immediately and is added to the order book. Since your order increases liquidity in the order book, you are the “creator” of liquidity (maker).
Limit orders are usually executed as maker orders, but not always. Let's say you place a buy limit order with a limit price that is significantly higher than the current market price. Since an order can be filled at or above the limit price, your order will be filled at the market price (since it is lower than the limit price you set).
When you place an order with immediate execution, you become a taker. Your order is not added to the order book, but is immediately matched to an existing order from the order book. Since you are taking liquidity from the order book, you become a taker. Market orders are always taker orders because your order is executed at the best market price available at that time.
Some exchanges use a tiered fee model to incentivize traders to provide liquidity. Attracting high volume traders is one of the most important interests of any exchange. Liquidity begets more liquidity. In such systems, makers typically pay lower fees than takers because makers are the ones who add liquidity to the exchange. In some cases, exchanges may offer discounts on maker fees. You can check your current Binance commission level on this page.
If you are interested in learning more, read our article “Who are Makers and Takers?”
What is a bid-ask spread?
The bid-ask spread is the difference between the highest buy (ask) order price and the lowest sell (ask) order price for a given market. Essentially, it is the gap between the highest price at which a user is willing to sell and the lowest price at which a buyer is willing to buy.
The bid-ask spread is a way of measuring market liquidity. The smaller the spread between the bid and ask prices, the more liquid the market. The bid-ask spread can also be considered as a measure of supply and demand for a given asset.
When you place a market buy order, it will be filled at the lowest available ask price. Conversely, when you place a market sell order, it will be filled at the highest available buy price.
What are candlestick charts?
A candlestick chart is a graphical representation of the price of an asset on a given timeframe. It consists of candles, each of which represents a certain period of time. For example, if you select a one-hour time frame, the chart will display candles, each representing a period of one hour. On a one-day chart, candles mean a period of one day and so on.
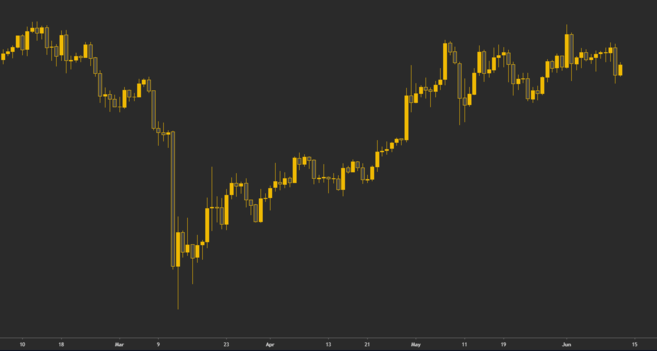
Bitcoin daily chart. Each candle represents one trading day.
A candlestick consists of four points: open, high, low and close (these values are also called OHLC). Open and close are the first and last recorded prices within the selected time frame, while low and high are the lowest and highest recorded prices, respectively.
Candlestick charts are one of the most important tools for analyzing financial data. Candlesticks originated in 17th century Japan, but were refined in the early 20th century by market trading pioneers such as Charles Dow.
Analyzing candlestick charts is one of the most common ways to study the Bitcoin market using technical analysis. Want to learn how to read candlestick charts? Check out the article “Candlestick chart. A Beginner's Guide."
What are candlestick charts?
Technical analysis is largely based on the assumption that previous price movements can help predict future price movements. So how do you use candlesticks for technical analysis? The goal is to identify patterns in candlestick charts and develop trading strategies based on them.
Candlestick charts help traders analyze market structure and differentiate between bullish and bearish stages of the market. They can also be used to identify areas of interest on a chart, such as support or resistance levels or potential turning points. These are the places on the chart where you can usually see increased trading activity.
Candlestick patterns are also a great way to manage risk as they provide specific and precise trading setups. How does this happen? Candlestick patterns can identify clear price targets and invalidation points. This allows traders to set very precise and controlled trading setups. This is why candlestick patterns are widely used by Forex traders and in the cryptocurrency industry.
The most common candlestick patterns include flags, triangles, wedges, hammers, stars and doji stars. If you want to learn how to understand charts, check out the following Binance Academy articles: 12 Popular Candlestick Patterns Used in Technical Analysis and A Beginner's Guide to Classic Chart Patterns.
What is a trend line?
Trendlines are a tool widely used by both traders and technical analysts. These are lines connecting specific data points on a graph. This is usually price data, but not always. Some traders may also use trend lines for technical indicators and oscillators.
The main purpose of trendlines is to visualize certain aspects of price action. In this way, traders can determine the overall trend and structure of the market.

Bitcoin price touches the trend line several times, indicating an uptrend.
Some traders use trend lines solely to better understand market structure. Some use them to create effective trading strategies based on how trend lines interact with price.
Trendlines can be applied to a chart on any timeframe. However, as with any other market analysis tool, trend lines on higher time frames are usually more reliable than those on lower time frames.
Another important aspect is the strength of the trend line. According to the traditional definition, a trend line must touch price at least two or three times to become valid. As a rule, the more times the price has touched (tested) the trend line, the more reliable it is considered.
If you want to learn more about how to draw trend lines, read the article Trend Lines.
What is support and resistance?
Support and resistance are some of the most basic concepts associated with trading and technical analysis.
Support means the level at which the price breaks the floor. In other words, a support level is an area of significant demand that buyers enter and push the price up.
Resistance means the level at which the price reaches the ceiling. A resistance level is an area of significant supply that sellers enter and push the price down.

The support level (red) is tested and broken, moving into the resistance level.
Now you know that support and resistance are levels of increased demand and supply, respectively. However, many other factors come into play when calculating support and resistance.
Technical indicators such as trend lines, moving averages, Bollinger Bands, Ichimoku clouds and Fibonacci retracement can also indicate the potential significance of support and resistance levels. In fact, even aspects of human psychology are used. This is why traders and investors incorporate support and resistance into their individual trading strategies in different ways.
Want to learn how to draw support and resistance levels on a chart? Read the article “Introduction to Support and Resistance Levels.”
Chapter 5 – Technical Analysis Indicators
Content
What is an indicator in technical analysis?
Leading and lagging indicators
What is a momentum indicator?
What is trading volume?
What is Relative Strength Index (RSI)?
What is a moving average (MA)?
What is the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator?
What are Fibonacci levels?
What is Stochastic RSI (StochRSI)?
What are Bollinger Bands (BB)?
What is Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP)?
What is a parabolic SAR system?
What is the Ichimoku cloud?
What is an indicator in technical analysis?
Technical indicators calculate metrics related to financial instruments. This calculation can be based on price, volume, on-chain data, open interest, social indicators, or even another indicator.
As we said earlier, technical analysts base their methods on the assumption that historical price patterns can determine future price movements. Thus, technical analysis traders can use a set of technical indicators on a chart to identify potential entry and exit points.
Technical indicators can be classified in several ways. There are indicators that indicate future trends (leading indicators), confirm an existing pattern (lagging indicators), or clarify events in real time (coincident indicators).
Other classifications characterize indicators from the point of view of information presentation. According to this classification, there are trend indicators that overlay data on the price, and there are oscillators that fluctuate between a minimum and maximum value.
There are also specific types of indicators that aim to measure a specific aspect of the market, such as momentum indicators. As the name suggests, they aim to measure and display market dynamics.
Which of the existing technical analysis indicators is the best? There is no easy answer to this question. Traders can use many different types of technical indicators, and their choice largely depends on their individual trading strategy. However, to make this choice, you must first learn about them. Our next chapter will be devoted to this.
Leading and lagging indicators
As we have already said, different indicators have different qualities and should be used for specific purposes. Leading indicators indicate future events. Lagging indicators are used to confirm what has already happened. How should they be used?
Leading indicators are generally useful for short- and medium-term analysis. They are used when analysts hypothesize a trend and are looking for statistical tools to confirm their hypothesis. When it comes to economics, leading indicators can be especially useful for predicting periods of recession.
In terms of trading and technical analysis, leading indicators can also be used for forecasting. However, no specific indicator can predict the future, so such forecasts should always be taken with a grain of salt.
Lagging indicators are used to confirm events and trends that have already occurred or are occurring. They may seem unnecessary, but they can also be very useful. Lagging indicators draw attention to certain aspects of the market that would otherwise remain hidden. Thus, lagging indicators are usually used to analyze long-term charts.
Want to know more? Read the article “Leading and Lagging Indicators.”
What is a momentum indicator?
Momentum indicators measure and display market momentum. What is market momentum? In simple terms, it is a measure of the rate at which prices change. Momentum indicators aim to measure the rate at which prices are rising or falling. They are typically used in short-term analysis by traders who want to profit from spikes in high volatility.
The goal of a momentum trader is to enter trades when momentum is high and exit when market momentum begins to fade. If volatility is low, the price is usually trapped in a small range. As tension builds, price often makes a strong impulsive move, eventually breaking out of the range. This is what momentum traders take advantage of.
After the move is complete and traders exit their positions, they switch to another asset with high momentum and try to play the same pattern. Thus, momentum indicators are widely used by day traders, scalpers and short-term traders who are looking for quick trading opportunities.
What is trading volume?
A typical indicator is trading volume. It shows the number of orders traded in pairs with an asset over a certain period of time. In other words, it shows how much of the asset changed hands during the measured time.
Some consider trading volume to be the most important technical indicator. “Volume precedes price” is a well-known phrase in the trading world. The implication is that high trading volume is a leading indicator indicating a large price movement (regardless of direction).
Using the trading volume indicator, traders measure the strength of the main trend. If high volatility is accompanied by high trading volume, this can be considered confirmation of the move. And this makes sense: high trading activity means significant volume, since many traders and investors are active at a particular price level. If volatility is not accompanied by high trading volume, the underlying trend can be considered weak.
Price levels with historically high volume can also be a good potential entry or exit point for traders. Since history tends to repeat itself, increased trading activity may occur at these levels. Ideally, support and resistance levels should also be accompanied by an increase in volume, confirming the strength of the level.
What is Relative Strength Index (RSI)?
Relative Strength Index (RSI) is an indicator that shows whether an asset is overbought or oversold. This is a momentum oscillator that shows the rate of price change. It is given a range from 0 to 100 and is usually shown as a line on a graph.

RSI indicator on the Bitcoin chart.
What is the idea behind measuring market dynamics? If market dynamics increase and the price rises, then the uptrend can be considered strong. And vice versa: if market dynamics decrease while the price increases, then the upward trend will be weak. In this case, a reversal may occur.
Let's look at how the traditional interpretation of the RSI indicator works. When the RSI value is below 30, the asset is considered oversold. An asset will become overbought when the RSI is above 70.
However, the RSI indicator should be taken with a certain amount of skepticism. RSI can reach extreme values under unusual market conditions - and even then, the current market trend may continue for some time.
RSI is one of the simplest technical indicators, which makes it one of the best for beginner traders. If you are interested in learning more, read our article “What is the RSI indicator?”
What is a moving average (MA)?
Moving averages smooth out price action and make spot market trends easier to spot. Because they are based on previous price data, they lack precision in being able to predict future price movements. Moving averages are lagging indicators.
Moving averages come in different types. The most common are the simple moving average (SMA or MA) and the exponential moving average (EMA). What is the difference?
A simple moving average is the arithmetic average of the price over the previous n periods. For example, to calculate the 10-day SMA, the average price of the last 10 days is taken and displayed on the chart.

200 week moving average for Bitcoin price.
The exponential moving average is a little more complicated. When calculating it, a different formula is used, in which more recent price data is important. As a result, the EMA reacts more quickly to recent price movements, while the SMA may take longer to reflect them.
As we have already said, moving averages are lagging indicators. The longer the period over which the chart is built, the longer the delay. Thus, the 200-day moving average will be slower to react to price reversals than the 100-day.
Moving averages help you easily identify market trends. If you want to learn more about them, read the article “What are moving averages.”
What is the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator?
MACD is an oscillator that displays market momentum based on two moving averages. Since it tracks price movements that have already taken place, it is a lagging indicator.
MACD consists of two lines - the MACD line and the signal line. How are they calculated? The MACD line is calculated by subtracting the 26 EMA from the 12 EMA. It's simple. Then the 9 EMA – signal line – is plotted on the chart with the MACD line. In addition, many charting tools also show a histogram showing the distance between the MACD line and the signal line.

MACD Indicator on Bitcoin Charts.
Traders use MACD by analyzing the relationship between the MACD line and the signal line. When analyzing MACD, a significant event is the intersection of two lines. If the MACD line crosses the signal line, it can be interpreted as a bullish signal. If the MACD line goes below the signal level, it can be interpreted as a bearish signal.
MACD is one of the most popular technical indicators for measuring market dynamics. If you want to learn more, check out the article “How the MACD Indicator Works.”
Thinking about where to start working with cryptocurrencies? Buy Bitcoin on Binance!
What are Fibonacci levels?
The Fibonacci Retracement (or Fib Retracement) tool is a popular indicator based on a sequence of numbers called the Fibonacci sequence. These numbers were defined back in the 13th century by the Italian mathematician Leonardo Fibonacci.
Fibonacci numbers are the basis for many technical analysis indicators, and the Fibonacci retracement is one of the most popular indicators of its kind. This indicator uses ratios derived from Fibonacci numbers and expresses them as a percentage. The resulting percentages are plotted on a chart and traders can use them to identify potential support and resistance levels.
These are the percentages:
0 %
23,6 %
38,2 %
61,8 %
78,6 %
100 %
Technically, the 50% level is not a Fibonacci ratio, but many traders take it into account when using the indicator. Fibonacci ratios outside the 0 – 100% range can also be used. The most common ones are 161.8%, 261.8% and 423.6%.

Fibonacci levels on the Bitcoin chart.
So how do traders use Fibonacci retracement levels? The basic idea of plotting percentages on a graph is to find an area of interest. Typically, traders select two major price points on the chart and attach the 0 and 100 values of the Fibonacci retracement tool to them. The range indicated by these points indicates potential entry and exit points and also helps determine stop loss order levels.
The Fibonacci Retracement tool is a universal indicator that can be used in a variety of trading strategies. If you're interested in learning more, read our article: A Guide to Fibonacci Retracement Levels.
What is Stochastic RSI (StochRSI)?
Stochastic RSI, or StochRSI, is an indicator derived from RSI. As with RSI, the main purpose of the indicator is to determine the level of overbought or oversold of an asset. However, unlike RSI, StochRSI is not generated from price data, but from RSI values. When using most charting tools, StochRSI values will range from 0 to 1 (or 0 to 100).
The StochRSI indicator is most useful when located near the top or bottom of a range. But due to the high update rate and high sensitivity, the indicator can produce many false signals that are difficult to interpret.
The traditional interpretation of the StochRSI indicator is somewhat similar to the RSI. When the indicator value exceeds 0.8, the asset can be considered overbought. When the indicator value is below 0.2, the asset can be considered oversold. However, we note that they should not be considered as direct signals for entering or exiting positions. Of course, the information from the indicator is important, but it is also important to interpret it correctly. This is why most technical analysis tools are best used in combination with other market analysis methods.
Want to learn more about StochRSI? Check out the article Stochastic RSI Explained.
What are Bollinger Bands (BB)?
Bollinger Bands, named after John Bollinger, are a way to measure market volatility and are often used to identify overbought and oversold conditions. This indicator consists of three lines, or “bands”: the SMA (middle band), and the upper and lower bands. The bands are placed on the price action chart. The idea is that as volatility increases or decreases, the distance between these bands changes, widening and contracting accordingly.

Bollinger Bands on the Bitcoin chart.
Let's look at the general interpretation of Bollinger Bands. The closer the price is to the upper band, the closer the asset may be to an overbought situation. Similarly: the closer it is to the lower band, the closer the asset may be to an oversold situation.
It should be noted that usually the price is within the bands, but sometimes it can go higher or lower. Does this represent an immediate buy or sell signal? No. This simply means that the market is moving away from the middle band of the SMA, reaching extreme conditions.
Bollinger Bands can also be used to try to predict a market squeeze, known as a Bollinger Band squeeze. It signifies a period of low volatility when the bands come very close to each other and “squeeze” the price into a small range. When "pressure" builds in this small range, the market will eventually jump out of the range, leading to a period of increased volatility. Since the market can then move up or down, the squeeze strategy is considered neutral (neither bearish nor bullish). Therefore, this instrument should be combined with other trading instruments, such as support and resistance.
Want to deepen your knowledge of Bollinger Bands? Read the article “What are Bollinger Bands?”
What is Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP)?
As we have already said, for many traders the most important indicator is trading volume. So what indicators are based on volume?
Volume-weighted average price, or VWAP, combines the power of volume with price action. In practical terms, it is the average price of an asset over a given period, weighted by volume. This makes it more useful than just average price since it takes into account which price levels have had the most trading volume.
How do traders use VWAP? VWAP is typically used to analyze the current market outlook. That is, if the market is above the VWAP line, it can be considered bullish. On the contrary, if the market is below the VWAP line, it can be considered bearish. Doesn't it remind you of the interpretation of moving averages? VWAP can indeed be compared to moving averages, at least in the way it is used. The main difference is that VWAP takes into account trading volume.
In addition, VWAP can also be used to identify areas of higher liquidity. Many traders use a price break above or below the VWAP line as a trading signal. However, they typically include other risk mitigation metrics in their strategy.
Want to learn more about how to use VWAP? Read the article “What is weighted average price (VWAP)”.
What is a parabolic SAR system?
The parabolic time/price system (parabolic SAR) is used to determine trend direction and potential reversals. "SAR" is an abbreviation for "Stop and Reverse." The indicator refers to periods when a long position should be closed and a short position should be opened, or vice versa.
Parabolic SAR is displayed on the chart as a series of points located above or below the price. If the dots are below the price, it means the price is in an uptrend. On the contrary, if the dots are above the price, it means the price is in a downtrend. A reversal occurs when the points move to the “other side” of the price.

Parabolic SAR indicator on the Bitcoin chart.
Parabolic SAR provides insight into the direction of the market trend. In addition, it is convenient for determining trend reversal points. Some traders use the Parabolic SAR indicator for a trailing stop loss. This special order type moves with the market and ensures that investors can protect their profits during a strong uptrend.
Parabolic SAR works best during strong market trends. During periods of consolidation, it provides many false signals for potential reversals. Want to know how to use the Parabolic SAR indicator? Check out <em>"Quick Guide to Using a Parabolic SAR System."
What is the Ichimoku cloud?
Ichimoku Cloud is a TA indicator that combines many indicators on one chart. Of all the indicators we have examined, Ichimoku is certainly one of the most complex. At first glance, it may be difficult to understand its formulas and how it works. But in practice, the Ichimoku cloud is not as difficult to use as it seems, and many traders choose it because it generates very clear trading signals.
As we have already said, the Ichimoku cloud is not just an indicator, but a set of indicators. The system provides insight into market momentum, support and resistance levels, and trend direction. This is achieved by calculating five averages and plotting them on a graph. The indicator creates a "cloud" of these averages that can forecast potential areas of support and resistance.
While averages play an important role, the key part of the indicator is the cloud itself. If the price is above the cloud, the market can be considered to be in an uptrend. Conversely, if the price is below the cloud, it can be considered to be in a downtrend.

The Ichimoku cloud on the Bitcoin chart acts first as support and then as resistance.
The Ichimoku cloud can also enhance other trading signals.
The Ichimoku cloud is quite difficult to master, but once you understand how it works, it is likely to start delivering great results. To learn more about it, read the article “How the Ichimoku Cloud Works.”
Chapter 6 – Cryptocurrency Trading Tips
Content
How to start trading cryptocurrency?
How to trade cryptocurrency on Binance
What is a trade journal and should you use one?
How to calculate position size in trading?
Which online trading software should you use?
Should you join paid trading groups?
What is pump and dump?
Is it worth participating in cryptocurrency airdrops?
How to start trading cryptocurrency?
If you have decided to start trading cryptocurrency, here are a few things to consider.
First, you will of course need capital to trade. If you don't have savings, losing your funds can have a serious impact on your life. Remember: you should only trade with money that you are willing to lose. Trading is a complex process, and the vast majority of new traders lose their money. Always remember that the money you set aside for trading can quickly run out and you may never be able to recover your lost assets. It is recommended to start with small capital so that mistakes made are not so painful.
You also need to think about your overall trading strategy. There are many opportunities to make money in the financial markets. Depending on the time and effort you put into trading, you can choose between different strategies to achieve your financial goals.
And one moment. Many traders feel more comfortable if trading is not their main source of income. It is easier for them to cope with experiences if their daily life does not depend on its results. Eliminating emotions is a common trait of all successful traders, and it is much more difficult when your livelihood is at stake. So (especially if you're new) try to treat trading and investing as a side hustle. And start learning and practicing with small amounts. It may also be helpful to explore ways to earn passive income using cryptocurrency.
You can learn about the simplest mistakes in trading and technical analysis from the article “7 Common Mistakes in Technical Analysis (TA).”
How to trade cryptocurrency on Binance
So, you've decided that you want to dive into the world of cryptocurrency trading. What do you need to do?
First, you need to convert your fiat currency to cryptocurrency. The easiest way to do this is to go to the Buy Crypto page 1 on Binance where you will have a variety of options. You can purchase cryptocurrency using debit and credit cards, using a bank account on a P2P exchange, or through third-party solutions such as Simplex, Paxful or Koinal. When you finish, you will become part of the new financial system!
Now, with cryptocurrency, you have many options. So, for example, you can go to the Binance spot exchange and trade coins right now. If you already have trading experience, you can try the Binance or Binance Futures margin trading platform. You also have passive income opportunities that include staking, lending assets on Binance Savings, joining a Binance mining pool, and more.
All these features are available on so-called centralized exchanges, in particular Binance. These are the type of exchanges where you deposit cryptocurrency and conduct financial activities within the exchange's internal systems. However, thanks to the magic of blockchain, there are other options called decentralized exchanges (DEXs). With these sites, your funds never leave your own cryptocurrency wallet, so you always have full control over them. You can also connect a hardware wallet and trade directly from it.
Centralized exchanges dominate the cryptocurrency space. But many traders and blockchain enthusiasts believe that in the future, a significant portion of cryptocurrency trading volume will take place on DEXs. Head over to Binance DEX for a new trading experience!
What is a trade journal and should you use one?
A trading journal is a documentation of your trading activities. Is it worth having? It's better to have. You can use any tool - from a simple Excel spreadsheet to a subscription to a special service.
Some traders believe that keeping a trading journal plays an important role in achieving consistent profits, especially when it comes to more active trading. After all, if you don't document your trading activities, how can you identify your strengths and weaknesses? Without a trading journal, you won't have a clear picture of your trading results.
Remember that biases can play an important role in your trading decisions, and a trading journal can help mitigate some of them. How exactly? It’s very simple, because you can’t argue with the facts! All trading metrics come down to numbers, and if you don't succeed, it will reflect in your numbers. By keeping a meticulous trading journal, you can track which strategies work best.
How to calculate position size in trading?
One of the most significant aspects of trading is risk management. Some traders argue that this is generally the most important thing in trading. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate the position size using a standard formula. Here's how they're calculated.
First, you need to determine how much of your account you are willing to risk on individual trades. Let's say it's 1%. Does this mean you enter positions with 1% of your account? No, this means that if your stop loss is triggered, you will lose no more than 1% of your account.
This portion of funds may seem like a small amount, but it ensures that the inevitable few bad trades won't wipe out your account. So, once you determine this, you need to set your stop loss level. You set it for each individual transaction, based on the specifics of your trading strategy. Let's say you are going to set a stop loss of 5% of your initial investment. This means that when your stop loss is triggered and you exit with 5% of your entry, you will have lost exactly 1% of your account.
Let's say your account balance is 1000 USDT. We risk 1% on every trade. Our stop loss is 5% of the entry. What position size should we set?
1000 * 0,01 / 0,05 = 200If we only want to lose 10 USDT, which is 1% of our account, we must enter a position of 200 USDT.
This process may seem a little lengthy at first, but it is essential to proper risk management. Good news: we have a whole article dedicated to this, “How to calculate position size in trading.”
Which online trading software should you use?
Chart analysis is a core part of any technical analyst's arsenal. Where is the best place to do this? Binance integrates TradingView charts, so you can conduct analysis directly on the platform - both in the web interface and in the mobile application. You can also create an account on TradingView and check all Binance markets through their platform.
There are many other online charting programs on the market, each providing different benefits. But most likely, you will have to sign up for a paid monthly subscription. Tools focused on cryptocurrency trading include Coinigy, TradingLite, Exocharts, and Tensorcharts.
Should you join paid trading groups?
Most likely no. There are many great free sources of trading information out there, why not learn from them? It is also useful to practice trading on your own so that you can learn from your mistakes and find what best suits you and your trading style.
Joining a paid group can be a good learning tool, but beware of scams and false advertising. After all, trading results are very easy to fake to attract new users.
It is also worth considering why a successful trader would want to create a paid group. Of course, side income is always welcome, but why charge a huge tuition fee if they are already doing well?
Of course, we know of examples where successful traders have created first-class paid communities with additional services, such as the addition of special market data. Still, be careful and careful when giving your money to someone. Most paid trading groups exist to make money from new traders.
What is pump and dump?
Pump and dump is a scheme that involves inflating the price of an asset through false information. When the price has increased significantly ("pumped"), the attackers sell ("dump") cheaply purchased bags of coins at a much higher price.

Typical price movement according to a pump and dump pattern.
Pump and dump schemes are common in cryptocurrency markets, especially in bull markets. At this time, many inexperienced investors enter the market and it is easier to take advantage of them. This type of scam is most common among cryptocurrencies with small market capitalizations, as their prices tend to be easier to raise due to the low liquidity of these markets.
Pump and dump schemes are often organized by private "pump and dump groups" that promise easy profits for participants (usually in exchange for a reward). However, as a rule, members of such groups are used by an even smaller group of people who have already gained positions in coins and are waiting for the right moment to sell them.
In traditional markets, people found guilty of facilitating pump and dump schemes are subject to hefty fines.
Thinking about where to start working with cryptocurrencies? Buy Bitcoin on Binance!
Is it worth participating in cryptocurrency airdrops?
You can, but be especially careful! Airdrops are a new way to distribute cryptocurrency to a wide audience. An airdrop is a great way to ensure that cryptocurrency is not centralized in the hands of a few hodlers. Having a large number of independent hodlers is paramount to a healthy decentralized network.
Free cheese only comes in a mousetrap. Well, not only... Perhaps... If you are very lucky... However, most likely, the airdrop organizers will immediately try to take advantage of you or want to get something in return.
What can they ask for? One of the most common “assets” requested in exchange for a giveaway is your personal information. Is your personal data worth $10 – $50 in a highly speculative cryptocurrency? The choice is yours, but there are better ways to earn extra income without compromising your privacy and your personal data. So again, be especially careful when deciding to participate in a cryptocurrency airdrop.
Summary
We learned a lot, didn't we? Getting started trading cryptocurrencies can be challenging as there are a lot of concepts to learn. We hope this guide has helped you feel more comfortable with cryptocurrency trading.
However, there is always something to learn! That's why we created a platform for questions and answers about cryptocurrencies: Ask Academy. If you have more questions about cryptocurrency trading, blockchain technology, cryptography, or other related topics, feel free to post them. The community will definitely answer you! See you at Ask Academy.



