Departments
Introduction to Bitcoin
Where Do Bitcoins Come From?
Getting Started Using Bitcoin
Bitcoin Halving
Common Misinformation About Bitcoin
Bitcoin Scalability
Joining the Bitcoin Network
Part 1 - Introduction to Bitcoin
Contents
What is Bitcoin?
What is Bitcoin used for?
What makes Bitcoin valuable?
How does Bitcoin work?
What is Blockchain?
Is Bitcoin legal?
Bitcoin in Tarihi
Who created Bitcoin?
Did Satoshi create Blockchain technology?
Digital currencies before Bitcoin
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a type of digital money. But unlike the fiat currencies you are used to, there is no central bank controlling Bitcoin. Instead, the financial system in Bitcoin is run by thousands of computers spread around the world. Any person can join the ecosystem by downloading the open source software.
Announced in 2008 (and launched in 2009), Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency. It allows users to send and receive digital currency (bitcoin, with lowercase b, or BTC). What makes Bitcoin so attractive is that it cannot be censored, funds cannot be spent more than once, and transactions can be made from anywhere at any time.
What is Bitcoin used for?
People use Bitcoin for many different reasons. Many people prefer Bitcoin due to its permissionless nature (anyone with an internet connection can send and receive bitcoins). In this respect it is partly similar to cash because no one can stop you from using it. On the other hand, thanks to its digital structure, it can be transferred anywhere in the world.
What makes Bitcoin valuable?
Bitcoin is decentralized, censorship-resistant, secure and borderless.
These features make it attractive for use areas such as international foreign exchange transfers and payments, where individuals do not want to disclose their identities (sharing of identity information is mandatory when using a debit or credit card).
Many people choose to hold their bitcoins long-term rather than spend them (also known as hodling). Bitcoin is also referred to as digital gold due to its limited supply. Some researchers view Bitcoin as a store of value. Because it is rare and difficult to produce, it is likened to precious metals such as gold and silver.
Bitcoin investors believe that these features, combined with global availability and high liquidity, make the coin an ideal store of value for long-term investments. These people believe that the value of Bitcoin will continue to rise over time.
How does Bitcoin work?
When Alice makes a transfer to Bob, the transaction does not occur in the traditional way. This transaction is not the digital equivalent of passing a dollar bill to another person. It's more like Alice writing on a piece of paper (for all to see) that she gave Bob a dollar. When Bob wants to send the same funds to Carol, Carol can see by looking at the paper that Bob has the money.
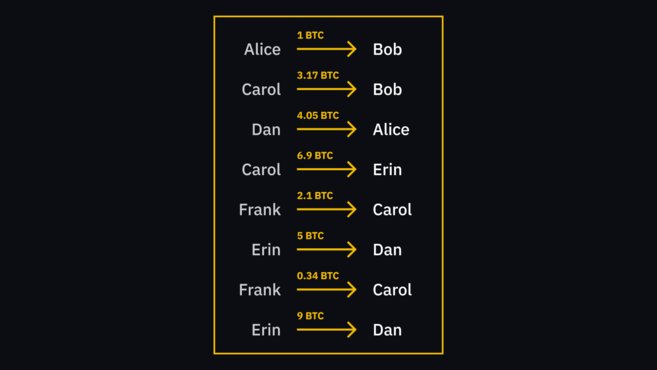
Paper is a special type of database called blockchain. All network participants maintain an exact copy of the blockchain on their devices. Participants connect to each other to synchronize new data.
When the user makes a payment, it broadcasts the transaction directly to the peer-to-peer network – there is no central bank or institution to process the transfers. The Bitcoin blockchain uses a special mechanism called mining to add new information. Adding new transaction blocks to the blockchain is done through the mining process.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is an append-only ledger: that is, only new data can be added to the ledger. Once information is added, it is extremely difficult to change or delete it. Blockchain achieves this by having each block contain a pointer to the block that came before it.
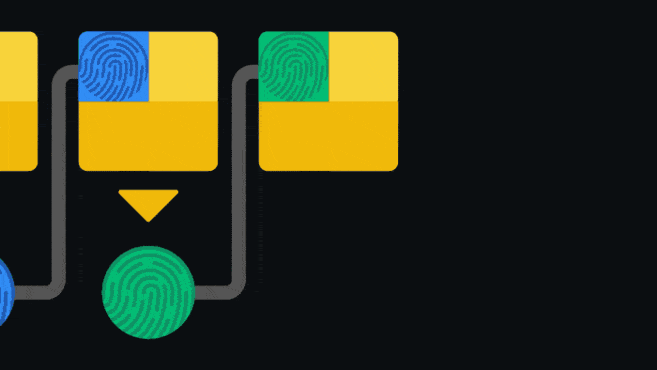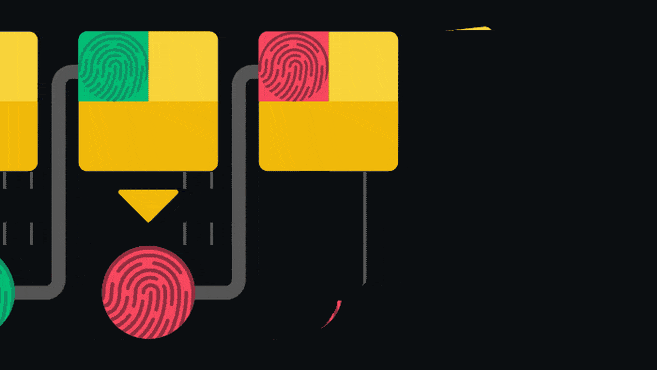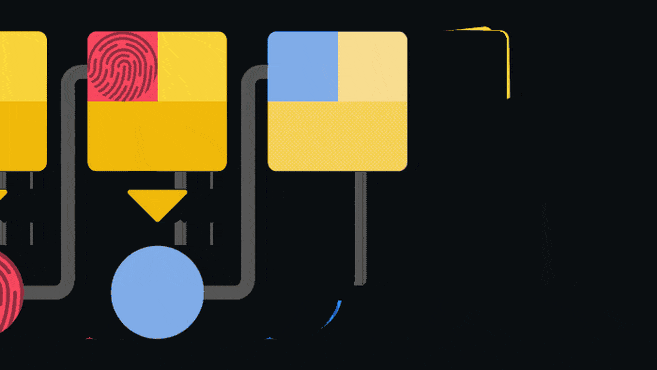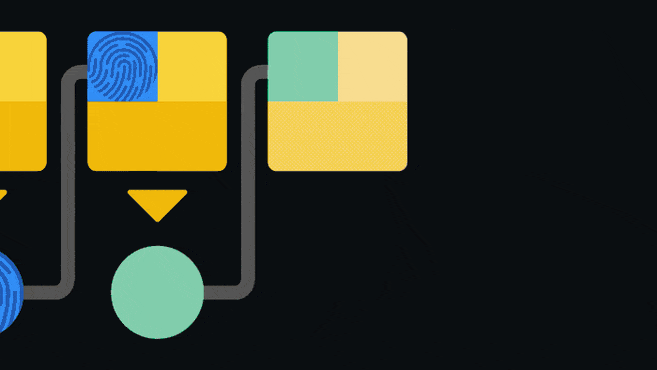
The pointer is actually a hash of the previous block. Hashing is passing data through a one-way function to create a unique “fingerprint” of the input. Even if a very small change is made to the input, the fingerprint will look completely different. Since the blocks are linked back to back, it is not possible for a person to change an old entry without invalidating subsequent blocks. This structure is one of the elements that make the blockchain secure.
For a general introduction to blockchains, you can read our Beginner's Guide to Blockchain Technology article.
Is Bitcoin legal?
Bitcoin is perfectly legal in most countries. But there are some countries that are exceptions, so be sure to read your country's laws on the subject before investing in cryptocurrencies.
In legal countries, governments' approaches to taxation and legal compliance vary. Regulations are still extremely inadequate in general, and this situation is likely to change significantly in the coming years.
Bitcoin in Tarihi
Who created Bitcoin?
Nobody knows! The creator of Bitcoin used the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, but there is no information about this person's identity. Satoshi can be a person or a group of developers anywhere in the world. The name is of Japanese origin, but Satoshi's mastery of English has led many to think that this person/group comes from an English-speaking country.
Satoshi released the software as well as the Bitcoin white paper. But the mysterious creator disappeared in 2010.
Did Satoshi create Blockchain technology?
Bitcoin actually combines several different technologies that have been in use for some time. The concept of blockchain was not born with Bitcoin. Immutable data structures like this are based on a system that Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta introduced in the early 1990s for timestamping documents. Similar to today's blockchains, this system uses cryptographic techniques to secure data and prevent it from being tampered with.
Interestingly, Satoshi's white paper does not use the concept of "blockchain" anywhere.
You can also check out the Blockchain History article.
Digital currencies before Bitcoin
Although Bitcoin is not the first attempt at digital currencies, it is undoubtedly the most successful. Earlier structures paved the way for Satoshi's discovery:
DigiCash
DigiCash is a company founded in the late 1980s by cryptographer and computer engineer David Chaum. It was introduced as a privacy-focused solution for online transactions, based on an article written by Chaum (described here).
The DigiCash model is a centralized system, but it is still a very interesting experiment. The company later went bankrupt. According to Chaum, this is because the system was introduced before e-commerce gained popularity.
B-money
B-money was first proposed by computer engineer Wei Dai in a paper published in the early 1990s. This article is also referenced in the Bitcoin white paper and it is quite clear why.
B-money is a Proof of Work system (used in Bitcoin mining) and offers the use of a distributed database where users can sign transactions. The second version of B-money describes an idea similar to staking used in other cryptocurrencies today.
Ultimately, B-money was never put into use because it did not pass the design phase. However, Bitcoin has clearly been influenced by the concepts introduced by Dai.
Bit Gold
Because there are so many similarities between Bit Gold and Bitcoin, some people believe that Nick Szabo, the creator of Bit Gold, is Satoshi Nakamoto. Bit Gold basically consists of a registry that records data series whose source is based on Proof of Work transactions.
Similar to B-money, it was never continued to be developed. However, due to its similarity to Bitcoin, it positions itself as a “precursor to Bitcoin”.
Part 2 - Where do Bitcoins come from?
Contents
How to create new bitcoins?
How many bitcoins are there in total?
How does Bitcoin mining work?
How long does it take to dig a block?
How to create new bitcoins?
Bitcoin has a limited supply, but not all units are in circulation yet. The only way to create new coins is through a process called mining. Mining is the specific mechanism for adding data to the blockchain.
How many bitcoins are there in total?
The protocol pegs the maximum supply of Bitcoin at 21 million coins. As of 2020, almost 90% of this amount has been created, but it will take a hundred years for the remaining coins to be created. This is due to a period of events called halvings that gradually reduce the mining reward.
How does Bitcoin mining work?
Participants add blocks to the blockchain through mining. To do this, they must dedicate a certain amount of computing power to solving a cryptographic puzzle. In return, participants who propose a valid block receive a reward as an incentive.
Creating a block is costly, but checking whether the block is valid is cheap. If someone tries to cheat with an invalid block, the network will immediately reject the block and the miner will not be able to recoup the mining costs he spent.
The reward, often referred to as the block reward, consists of two elements: transaction fees attached to transactions and the block allowance. The block allowance is the only source of “fresh” bitcoins. With each block mined, a certain amount of coins is added to the total supply.
How long does it take to dig a block?
The protocol adjusts the mining difficulty level so that it takes approximately ten minutes to find a new block. Blocks are not always found exactly ten minutes after the previous one, block times are more or less around that target.
Part 3 - Getting Started with Bitcoin
Contents
How can I buy Bitcoin?
How to buy Bitcoin with credit/debit card?
How to buy Bitcoin on peer-to-peer markets?
What can I buy with Bitcoin?
Where can I spend Bitcoin?
What happens if I lose my Bitcoins?
Can I reverse Bitcoin transactions?
Can I make money with Bitcoin?
How can I store my Bitcoins?
Keeping Bitcoins on Binance
Keeping coins in a bitcoin wallet
hot wallets
cold wallets
How can I buy Bitcoin?
How to buy Bitcoin with credit/debit card?
Binance allows you to buy Bitcoin seamlessly through your browser. To do this:
Go to the Buy and Sell Cryptocurrency portal.
Select the cryptocurrency you want to purchase and the currency you want to use for payment.
Log in to Binance or sign up if you don't have an account yet.
Choose your payment method.
If you are directed this way, enter your card information and complete identity verification.
That's it! Your Bitcoins will be deposited into your Binance account.
How to buy Bitcoin on peer-to-peer markets?
You can also buy and sell Bitcoin on peer-to-peer markets. This method allows you to buy coins from other users directly through the Binance mobile app. For this:
Open the app and log in or register.
Select the Buy tab in the upper left corner of the interface, then select One-click buy and sell.
You will be presented with different suggestions – click Get the one you prefer.
You can pay with other cryptocurrencies (With Cryptocurrency tab) or fiat currencies (With Fiat tab).
Below you will be asked for your payment method. You can choose the method you want.
Select Buy BTC.
You need to pay now. When you make the payment, click Mark as Paid and confirm.
The transaction is completed when the seller sends you your coins.
Do you want to enter the world of cryptocurrency? You can buy Bitcoin via Binance!
What can I buy with Bitcoin?
You can buy many things with Bitcoin. At this stage, it may be difficult (though not impossible) to find merchants who accept Bitcoin in brick-and-mortar stores. However, you can find websites that accept Bitcoin or allow you to purchase gift cards to use for other services.
To give a few examples, here are some of the things you can buy with Bitcoin:
Flight tickets
hotel rooms
Real estate
Food and drink
Clothes
gift card
Online subscriptions
Where can I spend Bitcoin?
The number of places where you can spend Bitcoin is increasing! To mention a few of them:
TravelbyBit
Save money on high credit card transaction fees while traveling the world! You can book flights and hotels using Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies through TravelbyBit. Sign up and get a 10% discount on bookings made with crypto.
He will spend
Spendabit is a search engine for products you can buy with Bitcoin. Search for what you want to buy and find a list of sellers where you can do it using Bitcoin.
Coinmap
Search for all cryptocurrency dealers and ATMs around you. If you want to spend Bitcoin but don't know where you can do it, Coinmap may be the ideal choice for you.
Bitrefill
Here you can buy gift cards for hundreds of services and add Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies to your phone. You can easily perform these transactions and use Lightning Network for your payments.

Current list of merchants accepting cryptocurrencies as payment. Source: https://coinmap.org/
What happens if I lose my Bitcoins?
Since there is no intermediary bank, you are responsible for keeping your coins safe. While some people prefer to keep their coins on exchanges, others prefer to take control through various wallets. If you are using a wallet, it is very important to save your seed phrase so that you can recover the wallet.
Can I reverse Bitcoin transactions?
Once data is added to the blockchain, it is not easy (in practice impossible) to remove it. This means that once you make a transaction, it is not possible to reverse it. You should always double or even triple check the address to make sure you are sending your funds to the correct address.
For an example of how you can theoretically reverse a transaction, see What is a 51% Attack? You can read the article.
Can I make money with Bitcoin?
You can make money with Bitcoin, but you can also lose money with Bitcoin. Generally, long-term investors buy and hold Bitcoin thinking that its price will increase. Others prefer to trade Bitcoin against other cryptocurrencies to make short- or medium-term profits. Both of these strategies are risky, but their returns are higher than lower-risk approaches.
Some investors adopt mixed strategies. It keeps some of the Bitcoins as a long-term investment and buys and sells some of them on a short-term basis (in a separate portfolio). There is no right or wrong way to allocate assets in your portfolio. Every investor will have a different risk preference and different goals.
Lending is an increasingly popular form of passive income. By lending your coins to another person, you can earn income from the interest they will pay at a later date. Platforms like Binance Lending allow you to do this for Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
How can I store my Bitcoins?
There are many ways to store coins, and each of these ways has its own strengths and weaknesses.
Keeping Bitcoins on Binance
An escrow solution is a method of custody where users do not hold the coins themselves, but instead trust a third party to hold the coins. To make a transaction, they must log in to the third party's platform. Exchanges like Binance often use this method because it is much more efficient in terms of trades.
Keeping your coins on Binance allows you to easily access your funds for trading or lending purposes.
Keeping coins in a bitcoin wallet
Non-escrow-based solutions give control of funds to the user. In this type of solution, you need to use a wallet to store the funds. The wallet does not directly hold the coins themselves. Instead, it holds a key that will unlock the coins on the blockchain. You have two options when it comes to wallets:
hot wallets
A hot wallet is software that connects to the internet via a route. It usually takes the form of a mobile or desktop application that allows you to easily receive and send coins. Trust Wallet is an example of a mobile wallet that is easy to use and supports many coins. Hot wallets are more convenient for payments because they are online, but they are also more vulnerable to attack.
cold wallets
Cryptocurrency wallets that do not connect to the internet are called cold wallets. These wallets are more vulnerable to attack because they have no online attack vector, but tend to offer a correspondingly more cumbersome user experience. Examples of cold wallets include hardware wallets or paper wallets.
For a more in-depth review of wallet types, see What Are the Types of Crypto Wallets? You can read our article.
Part 4 - Bitcoin Halving
Contents
What is Bitcoin Halving?
How does Bitcoin Halving work?
Why is Bitcoin Halving done?
What is the impact of Bitcoin Halving?
When is the next Bitcoin Halving?
What is Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin Halving is an event where block rewards are reduced. After the halving, the reward given to miners for validating new blocks is halved (they start receiving half the reward they used to receive). However, there will be no change in transaction fees.
How does Bitcoin Halving work?
When Bitcoin was launched, miners were rewarded with 50 BTC for each block they found.
The first halving was held on November 28, 2012. At this point, the protocol reduced the block reward from 50 BTC to 25 BTC. The second halving took place on July 9, 2016 (from 25 BTC to 12.5 BTC). The next one, expected to take place in May 2020, will reduce the reward to 6.25 BTC.
You may have noticed that a certain structure has emerged. Halving occurs every four years with a few months' play. This structure occurs by design, but the protocol does not specify a date for when the halving will occur. Instead, it takes block height into account – halving occurs every 210,000 blocks. So approximately every 2,100,000 minutes the allowance can be expected to be halved (remember, it takes about 10 minutes to mine a block).

From the chart above you can see how the block allowance has decreased over time and its relationship to the total supply. At first glance, it may seem like the rewards have dropped to zero and the maximum supply is already in circulation. But in reality this is not the case. The curves trend extremely close, but block rewards are expected to drop to zero by 2140.
Why is Bitcoin Halving done?
Halving is one of Bitcoin's main notable features, but Satoshi never fully explained the reasoning behind setting the supply at a maximum of 21 million units. Some think this is simply a result of starting block rewards at 50 BTC and halving the rewards every 210,000 blocks.
Having a limited supply means that the value of the currency will not tend to decline in the long run. This makes a big difference compared to fiat currencies, which lose purchasing power as new units are added to circulation.
It makes sense that the speed at which participants mine coins is limited. After all, 50% of coins were created in block 210,000 (in 2012). If the reward had remained at the same level, all of the blocks would have been mined in 2016.
The halving mechanism provides incentives for mining to continue for more than 100 years. This gives the system enough time to attract enough users for a fee market to emerge.
Do you want to enter the world of cryptocurrency? You can buy Bitcoin via Binance!
What is the impact of Bitcoin Halving?
Miners are most affected by halvings. This result is logical considering that the majority of miners' earnings consist of block allowances. After the halving, they start earning only half of the amount they previously received. Rewards also include transaction fees, but to date transaction fees have only made up a small portion of block rewards.
Therefore, halvings make it unprofitable for some participants to continue mining. What this means for the industry at large is unknown. The decrease in block rewards could lead to further increased centralization of mining pools or the emergence of more efficient mining practices.
If Bitcoin continues to use the Proof of Work algorithm, transaction fees must increase to keep mining profitable. This scenario is quite possible since blocks can only hold a certain number of transactions. If there are many pending transactions, those with higher transaction fees can be added to the block first.
In the past, there has been a sharp increase in Bitcoin prices following the halving. Of course, we do not have much data since there have only been two halvings to date. Many people think that price movements are due to Bitcoin's scarcity and that this awareness is triggered by the halving. Proponents of this theory believe that prices will rise sharply once again following the event in May 2020.
Others challenge this logic and believe that the market is already reflecting the halving (see Efficient Market Hypothesis). This event does not come as a surprise, it has been known to participants for more than a decade that the prize will be halved in May 2020. Another point is that the market was extremely underdeveloped in the first two halvings. Today, the market has a higher profile, offers sophisticated trading instruments and accommodates a larger pool of investors.
When is the next Bitcoin Halving?
The next halving is expected to occur in May 2020, reducing the reward to 6.25 BTC. You can track the remaining time with Binance Academy's Bitcoin Halving Countdown.
Part 5 - Common Misinformation About Bitcoin
Contents
Is Bitcoin anonymous?
Is Bitcoin a fraud?
Is Bitcoin a bubble?
Does Bitcoin use encryption?
Is Bitcoin anonymous?
Not really. Bitcoin may seem anonymous at first glance, but this is not true. The Bitcoin blockchain is public and transactions are visible to everyone. Your identity is not tied to your wallet address on the blockchain, but an observer with the right resources can connect the two. It is more accurate to describe Bitcoin as pseudonymous. Bitcoin addresses are visible to everyone, but the names of the address holders are not.
However, the system is relatively secretive and there are ways to make it difficult for observers to keep track of what you are doing with your bitcoins. Freely available technologies can “break the link” between addresses by creating plausible deniability. Additionally, future upgrades can also greatly improve privacy. For an example of this, you can read our Introduction to Confidential Transactions article.
Is Bitcoin a fraud?
No. Just like fiat currencies, Bitcoin can be used for illegal activities. But this does not make Bitcoin a fraud tool per se.
Bitcoin is a digital currency that is not controlled by anyone. Although its opponents call Bitcoin a pyramid scheme, it does not actually fit this definition. As a digital currency, it works equally well whether its value per coin is $20 or $20,000. It has been in use for over 10 years and the technology has proven to be extremely safe and reliable.
Unfortunately, Bitcoin is used for many types of scams that you need to be careful about. These may include techniques such as phishing, as well as other social engineering schemes such as fake giveaways and airdrops. As a general rule of thumb: if something feels too good to be true, it's probably a scam. Never share your private keys and seed phrase with anyone else, and be wary of offers to multiply your money on your behalf with little risk. If you send your coins to a scammer or a fake giveaway, you will lose those coins forever.
Is Bitcoin a bubble?
Throughout the many parabolic rises in prices, you may have frequently heard people refer to Bitcoin as a speculative bubble. Many economists compare Bitcoin to periods like Tulip Mania or the dot-com boom.
Due to Bitcoin's unique nature as a decentralized digital commodity, prices are determined entirely by speculation in the free market. Therefore, although there are many factors that affect the Bitcoin price, they ultimately affect market supply and demand. And because Bitcoin is rare and follows a strict release schedule, demand is thought to outstrip supply in the long run.
The cryptocurrency market is also relatively small compared to traditional markets. This means that Bitcoin and other crypto assets tend to be more volatile, with short-term market imbalances between supply and demand often occurring.
In other words, Bitcoin can sometimes be a volatile asset. But volatility is part of financial markets, especially those with low volume and liquidity.
Does Bitcoin use encryption?
No. It's a common misconception, but Bitcoin's blockchain does not use encryption. Each peer on the network must be able to read transactions to check if they are valid. Bitcoin uses digital signatures and hash functions instead. Some digital signature algorithms use encryption, but this is not the case for Bitcoin.
However, it is important to note that many apps and crypto wallets use encryption to protect users' wallets with passwords. However, these encryption methods have nothing to do with blockchain. These are only included in other blockchain-related technologies.
Chapter 6 - Bitcoin Scalability
Contents
What does scalability mean?
Why does Bitcoin need to scale?
What is Bitcoin's transaction capacity?
Lightning Network nedir?
What is a fork?
Soft fork
Hard fork
What does scalability mean?
Scalability is the ability of a system to grow to meet increasing demand. If you have a website that is receiving more demand than its capacity, you can scale the site by adding more servers. If you want to run more comprehensive applications on your computer, you can upgrade the parts of your computer.
In the context of cryptocurrencies, this term is used to refer to the ease of upgrading a blockchain to handle a larger number of transactions.
Why does Bitcoin need to scale?
Bitcoin needs to be fast to be used for everyday payments. In its current state, it has a low throughput, meaning the amount of transactions that can be made per block is limited.
As you may recall from the previous section, miners receive transaction fees as part of their block rewards. Users add these fees to their transactions to incentivize miners to add their transactions to the blockchain.
Miners prioritize transactions with higher transaction fees because they want to get a return on their investment in hardware and electricity. If there are a large number of transactions in the network's “waiting room” (called the memory pool), transaction fees can rise significantly as users will pay more to have their transactions included. In the worst case scenario, the average transaction fee can be up to 50 USD.
What is Bitcoin's transaction capacity?
Based on the average number of transactions per block, Bitcoin currently has approximately five transactions per second. This figure is quite low compared to centralized payment solutions, but this is the downside of using a decentralized currency.
Bitcoin has to limit the size of its blocks because it is not governed by a data center that a single person can upgrade at will. A new block size capable of processing 10,000 transactions per second could be integrated but in this case the decentralization of the network would suffer. Remember that full nodes need to download new information approximately every ten minutes. If the download process becomes too challenging for some nodes, these nodes may choose to remain offline.
Bitcoin advocates believe that effective scaling must be done in different ways if the protocol is to be used for payments.
Lightning Network nedir?
Lightning Network is a scaling solution for Bitcoin. This is called a second-layer solution because it moves transactions out of the blockchain. Instead of all transactions being recorded in the base layer, they are handled through another protocol built on top of the base layer.
Lightning Network allows users to send funds almost instantly and for free. There is no limit on transaction efficiency (assuming users have the capacity to receive and send). To use the Bitcoin Lightning Network, two participants lock their coins in a private address. The address has a unique feature – it only releases bitcoins if both parties agree.
From this point on, parties begin to keep a private ledger where they can make changes to balances without having to report them to the main chain. Users publish the transaction to the blockchain only after they are done with the private ledger. The protocol then updates the balances accordingly. It is not necessary for the two parties to have mutual trust. If a party tries to cheat, the protocol determines this and punishes it.
A payment channel like this requires the user to make only two on-chain transactions in total: one to fund the address and the other to distribute coins back to the addresses. This means that thousands of transactions can be made off-chain during this time. With further development and optimization, the technology could become an important element of large blockchain systems.
For more details on the scaling issue and potential solutions, you can read our article Blockchain Scalability – Sidechains and Payment Channels.
What is a fork?
Since Bitcoin is open source, anyone can make changes to the software. You can also add new rules and remove old ones according to different needs. But not all changes are the same: some updates make your node incompatible with the network, while others keep it backwards compatible.
Soft fork'lar
Soft forks are rule changes that allow updated nodes to interact with old nodes. Let's take block size as an example. Let's say we have block sizes of 2MB and half the network has implemented a change that now requires all blocks to be less than 1MB. In this case, all blocks larger than 1MB are rejected.
Old nodes can still receive these blocks or create their own blocks. This means that all nodes still remain part of the same network, regardless of the version they use.
You can see from the animation below that smaller blocks are accepted by both old and new nodes. However, new nodes do not accept 2MB blocks as they start working according to the new rules.

Bitcoin's Segregated Witness (or SegWit) is an example of a soft fork. Using a clever technique, a new format for blocks and transactions has been introduced. Old nodes continue to receive blocks but do not verify the new transaction type.
Hard fork'lar
Hard fork is more complicated. Let's say half the network wants to increase the block size from 2MB to 3MB. If you send a 3MB block to old nodes, it will be rejected because the rules clearly state that the maximum size they can accept is 2MB. The blockchain splits into two as the two networks are no longer compatible with each other.

The black chain in the above chart is the original one. Block 2 is the block where the hard fork took place. At this point, updating nodes start producing larger blocks (green ones). Old nodes do not recognize these new blocks, so they continue on a different path. There are now two blockchains, but they share a common history until Block 2.
Two different protocols emerge, each with its own currency. All balances from the old protocol are cloned. So if you have 20 BTC in the original chain, you will have 20 NewBTC in the new chain.
A controversial hard fork was made in Bitcoin in 2017 with a similar scenario above. A small portion of participants wanted to increase block size for greater efficiency and lower transaction fees. Others have argued that this is a poor scaling strategy. Ultimately, Bitcoin Cash (BCH) emerged from the Bitcoin network with a hard fork and had its own independent community and road map.
For more information about Forks, you can check out our Hard Forks and Soft Forks article.
Chapter 7 - Joining the Bitcoin Network
Contents
Bitcoin node'u nedir?
How does a Bitcoin node work?
Tam node'lar
Light nodes
Mining Nodes
How to become a full Bitcoin node?
How to mine Bitcoin?
How long does it take to mine a bitcoin?
Who can contribute to Bitcoin code?
Bitcoin node'u nedir?
“Bitcoin node” is the term used to describe a program that interacts with the Bitcoin network in some way. It can be anything from a mobile phone managing a Bitcoin wallet to a computer maintaining a full copy of the blockchain.
There are several different types of nodes, and each has its own functions. Each acts as a point of contact with the network. They transmit information about transactions and blocks within the system.
How does a Bitcoin node work?
Tam node'lar
A full node verifies whether transactions and blocks meet certain obligations (e.g. compliance with rules). Many full nodes use Bitcoin Core software, the reference implementation of the Bitcoin protocol.
Bitcoin Core is the program published by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009. At that time it was simply called Bitcoin, but was later renamed to avoid confusion. Other applications can also be used if they are compatible with Bitcoin Core.
Full nodes are crucial to Bitcoin's decentralization. They download blocks and transactions, verify them, and share them with the rest of the network. Users do not need third parties for anything, as they independently verify the accuracy of the information presented to them.
If a full node keeps a copy of the entire blockchain, this node is called a full archive node. But some users delete old blocks to save space – the Bitcoin blockchain contains more than 200GB of transaction data.

Distribution of Bitcoin full nodes around the world. Source: bitnodes.earn.com
Light nodes
Light nodes are not as extensive as full nodes, but these nodes require fewer resources. They allow users to interact with the network without having to do all the processing that a full node does.
Full nodes download entire blocks to verify, while lightweight nodes only download a portion of each block (this is called the block header). Although the block header is small in size, it contains information that allows users to check whether their transactions are in a particular block.
Light nodes are ideal for devices that have limitations on bandwidth or free space. These types of nodes are commonly used in desktop computers and mobile wallets. However, lightweight nodes are dependent on full nodes because they cannot verify.
Mining Nodes
Mining nodes are full nodes with the additional task of producing blocks. As we mentioned before, they need special equipment and software to add data to the blockchain.
Mining nodes take pending transactions and hash them with other information to create a number. If the number is below the target set by the protocol, the block is valid and can be broadcast to other full nodes.
However, miners must be full nodes in order to mine without needing anyone else. Otherwise, they have no way of knowing which transactions will be included in the block.
If a participant wants to mine but does not want to become a full node, they can connect to a server to provide them with the information they need. If you are mining in a pool (i.e. working with others) only one person needs to be a full node.
For more information about the different types of nodes, see What are Nodes? You can read our article.
How to become a full Bitcoin node?
Becoming a full node can be beneficial for developers, vendors, and end users. Running the Bitcoin Core client on your own hardware not only gives you privacy and security benefits, but also strengthens the Bitcoin network overall. With a full node, you can interact with the ecosystem without needing anyone else.
A small number of Bitcoin-focused companies offer plug-and-play nodes. A completed hardware is sent to the user, and the user simply has to turn it on to start downloading the blockchain. This method may be more useful for users with less technical expertise, but it is often much more expensive than installing your own hardware.
Most of the time, an old personal or desktop computer will suffice. It is not recommended to run node on the computer you use daily because it can seriously slow down the computer. You need to make sure you have enough memory to download the entire blockchain because it keeps growing.
A 1TB hard drive should last you for the next few years unless there is a significant change in block size. Other requirements are 2GB of RAM (most computers' default hardware is higher than this) and very high bandwidth.
At this stage, you can learn the details of the process of setting up your node from the Full Node Operation guide on bitcoin.org.
How to mine Bitcoin?
In the early days of Bitcoin, it was possible to create new blocks with a standard laptop. At the time, there was little competition in mining as the system was not recognized. Since there was very little mobility, the mining difficulty level set by the protocol was naturally low.
As the network's hash rates rose, participants had to upgrade to better equipment to stay competitive. Having gone through various types of hardware, the mining industry has finally entered the era of Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs).
As the name suggests, these devices are created for a special purpose. Although they are extremely efficient, they only serve one purpose. So a mining ASIC is a specialized computer used solely for mining. The Bitcoin ASIC can mine Bitcoin, but it cannot mine other coins that do not use the same algorithm.
Today, Bitcoin mining requires significant investment not only in hardware but also in energy. Currently a good mining device can process up to ten trillion transactions per second. Although very efficient, ASIC miners consume incredibly high amounts of electricity. It is very difficult to make a profit from Bitcoin mining unless you have access to some mining equipment and cheap electricity.
But it is quite easy to start your own mining operation with the materials. Most ASICs come with their own software. The most popular option is to direct your miners to a mining pool where they will work with others to find a block. If you are successful, a portion of the block rewards obtained will be yours in proportion to the hash rate you provide.
You can also choose solo mining where you work alone. The probability of creating a block decreases, but if you create a valid block, you keep all the rewards.
How long does it take to mine a bitcoin?
It is difficult to give a general answer as there are different variables to consider. How fast you can mine a coin depends on the amount of electricity you use and your hash rate. You also need to consider the expense of running a mining device.
To get an idea of the income from mining Bitcoin, it is recommended to determine the estimated costs using a mining calculator.
Who can contribute to Bitcoin code?
Bitcoin Core software is open source, meaning anyone can contribute the code. You can suggest new features to be added to the 70,000+ lines of code or evaluate existing features. You can also report software vulnerabilities or translate and improve documentation.
Changes made to the software go through a comprehensive evaluation process. After all, there shouldn't be any software vulnerabilities in software that handles hundreds of billions of dollars.
If you want to contribute to Bitcoin, you can check out our developer Jimmy Song's blog post explaining how to do this or the Bitcoin Core website.