Contents
What is crypto economy?
What problem does crypto economy solve?
The role of cryptoeconomics in Bitcoin mining
How does cryptoeconomics increase the security of Bitcoin?
crypto economic cycle
latest ideas
What is crypto economy?
In its simplest form, cryptoeconomics offers a way to coordinate the behavior of network participants by combining cryptography and economics.
More specifically, cryptoeconomics is a field of computer science that attempts to solve participant coordination problems in digital ecosystems through cryptographic and economic incentives.
It is important to consider cryptoeconomics when building centralized networks because it is the mechanism that provides a way to organize participants' incentives without the need for trusted third parties.
Rather than being a subset of traditional economics, cryptoeconomics is a blend of methods from game theory, mechanism design, mathematics, and other fields from economics. The main goal is to understand how to fund, design, develop and facilitate the operations of centralized networks.
This article will examine the roots of the crypto economy and the role of Bitcoin and other centralized networks in its design.
What problem does crypto economy solve?
Before the advent of Bitcoin, it was widely believed that it was impossible to create a consensual peer-to-peer network without becoming significantly vulnerable to attacks and errors.
This problem is commonly known as the Byzantine Generals Problem. It is a logical dilemma that demonstrates the importance of reaching consensus among different actors in distributed systems. The problem assumes that because some actors are untrustworthy, consensus can never be achieved, so the network cannot function as intended.
With the creation of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto solved this problem by introducing incentives to peer-to-peer networks.
Since then, decentralized networks continue to use cryptography to provide consensus on the current state and history of the network. Many networks also use economic incentives to encourage participants to behave in a certain way.
This synergy of cryptographic protocols with economic incentives enables a completely new ecosystem of secure and resilient decentralized networks.
The role of crypto economy in Bitcoin mining
The goal of Bitcoin is to create a value transfer network that accurately verifies the transfer of value, is immutable and censorship-resistant.
This is made possible by the mining process. In this process, miners who successfully verify a block of transactions are rewarded with bitcoin. Such an economic incentive encourages miners to behave honestly and makes the network more reliable and secure.
The mining process consists of solving a difficult mathematical problem based on a cryptographic hash algorithm. In this context, hashes are used to connect each block to the next block, creating a timestamped record of confirmed transactions. These records are called blockchain.
Hashes are also used in computational puzzles that miners compete to solve. Additionally, one of the consensus rules that transactions have to follow is that bitcoin can only be spent if a valid digital signature is created from a private key.
These technological rules for mining are related to the security requirements of the Bitcoin network, including preventing malicious actors from taking control.
How does cryptoeconomics increase the security of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin's security model is built around the principle of majority rule. This means that bad actors can potentially take control of the blockchain by seizing the majority of the network's computing power in an attack commonly known as a 51% attack.
In such a scenario, attackers can prevent new transactions from being confirmed or even reverse transactions entirely. However, gaining control of such a large hash power would be very costly, requiring a lot of hardware and a large amount of electricity consumption.
Cryptoeconomics is one of the reasons why Bitcoin is successful. Satoshi Nakamoto used assumptions to support incentives for the network's different classes of participants. The security of the system depends largely on the effectiveness of these assumptions about how network participants will respond to particular economic incentives.
Without the rigor of its cryptographic protocol, there would be no secure unit of account to reward miners. Without miners, the validity of the distributed ledger's transaction history could not be assured, unless that ledger was verified by a trusted third party, but that would negate one of Bitcoin's main advantages.
According to cryptoeconomic assumptions, the symbiotic relationship between miners and the Bitcoin network creates trust. But this does not guarantee that the system will continue to work in the future.
crypto economic cycle
The cryptoeconomic cycle is a holistic model of cryptoeconomics. It is published by Joel Monegro and shows the flow of intangible value between different classes of participants in such peer-to-peer economies.
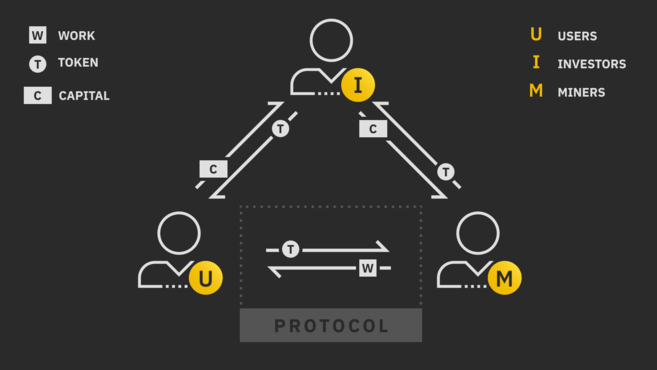
The model represents a three-sided market between miners (supply side), users (demand side) and investors (capital side). Each group exchanges value with each other using a rare cryptoeconomic resource (a token).
In the miner-user relationship in the loop, miners receive payment for their work with the tokens used by users. The network's consensus model protocol standardizes this process, while the cryptoeconomic model controls when and how miners receive payments.
Creating a network architecture governed by a distributed supply (miner) may be preferable as long as the benefits outweigh the disadvantages. Benefits generally include being censorship-resistant, the ability to conduct cross-border transactions, and greater reliability. However, decentralized systems tend to have lower performance compared to centralized systems.
In this model, the investor has two different tasks: providing liquidity to miners so they can sell their tokens, and providing money to the network by supporting token prices to be above mining costs.
The model illustrates these two roles by dividing investors into two groups: traders (short-term investors) and hodlers (long-term investors).
While traders provide liquidity for the token, allowing miners to sell their mined tokens and cover operational expenses, long-term investors support token prices and provide financial opportunity for the growth of the network. While the miner-trader relationship operates on the direct flow of value, the miner-trader relationship operates on the indirect flow of value.
This means that in such an economy, all participants need each other to achieve economic goals. Such a design creates a robust and secure network. It is more beneficial for an individual participant to comply with the incentivized set of rules than to act maliciously, which ultimately makes the network more resilient.
latest ideas
Although it emerged as a new concept with the birth of Bitcoin, crypto economy is an important building block that should be taken into account when designing decentralized networks.
Separating the different roles of the cryptoeconomic model helps analyze costs, incentives, and value streams for each participating group. Additionally, it helps evaluate relative power and identify centrality points that are important for designing a more balanced governance and token distribution model.
The field of cryptoeconomics and the use of cryptoeconomic models can be greatly beneficial in the development of future networks. By studying cryptoeconomic models that have already been tried and tested in live environments, future networks can be designed more efficiently and sustainably, thus creating a stronger decentralized economy ecosystem.